Page 251 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 251
TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT 231
that with other types of sensors. Furthermore, the
change in state is irreversible, except in the case of
liquid crystal displays. Even so, change-of-state sen-
sors can be handy when one needs confirmation that
the temperature of a piece of equipment or a material
has not exceeded a certain level, for instance, for
technical or legal reasons during product shipment.
. What are vapor pressure thermometers? How do they
work? Illustrate.
& Figure 8.6 illustrates vapor pressure thermometer.
& System is filled with gas, liquid, or vapor–liquid
mixture.
➢ Gas: Pressure is proportional to temperature.
➢ Liquid: Differential thermal expansion.
➢ Vapor–liquid mixture: Gauge reads vapor pres-
sure, which is a function of temperature.
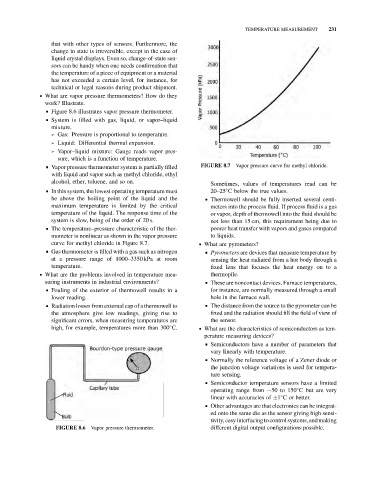
& Vapor pressure thermometer system is partially filled FIGURE 8.7 Vapor pressure curve for methyl chloride.
with liquid and vapor such as methyl chloride, ethyl
alcohol, ether, toluene, and so on. Sometimes, values of temperatures read can be
& In this system, the lowest operating temperature must 20–25 C below the true values.
be above the boiling point of the liquid and the & Thermowell should be fully inserted several centi-
maximum temperature is limited by the critical meters into the process fluid. If process fluid is a gas
temperature of the liquid. The response time of the or vapor, depth of thermowell into the fluid should be
system is slow, being of the order of 20 s. not less than 15 cm, this requirement being due to
& The temperature–pressure characteristic of the ther- poorer heat transfer with vapors and gases compared
mometer is nonlinear as shown in the vapor pressure to liquids.
curve for methyl chloride in Figure 8.7. . What are pyrometers?
& Gas thermometer is filled with a gas such as nitrogen & Pyrometers are devices that measure temperature by
at a pressure range of 1000–3350 kPa at room sensing the heat radiated from a hot body through a
temperature. fixed lens that focuses the heat energy on to a
. What are the problems involved in temperature mea- thermopile.
suring instruments in industrial environments? & These are noncontact devices. Furnace temperatures,
& Fouling of the exterior of thermowell results in a for instance, are normally measured through a small
lower reading. hole in the furnace wall.
& Radiation losses from external cap of a thermowell to & The distance from the source to the pyrometer can be
the atmosphere give low readings, giving rise to fixed and the radiation should fill the field of view of
significant errors, when measuring temperatures are the sensor.
high, for example, temperatures more than 300 C. . What are the characteristics of semiconductors as tem-
perature measuring devices?
& Semiconductors have a number of parameters that
vary linearly with temperature.
& Normally the reference voltage of a Zener diode or
the junction voltage variations is used for tempera-
ture sensing.
& Semiconductor temperature sensors have a limited
operating range from 50 to 150 C but are very
linear with accuracies of 1 C or better.
& Other advantages are that electronics can be integrat-
ed onto the same die as the sensor giving high sensi-
tivity,easyinterfacingtocontrolsystems,andmaking
Vapor pressure thermometer. different digital output configurations possible.
FIGURE 8.6