Page 255 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 255
CONDUCTION HEAT TRANSFER 235
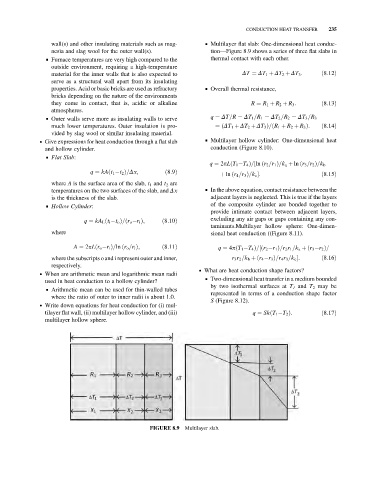
wall(s) and other insulating materials such as mag- & Multilayer flat slab: One-dimensional heat conduc-
nesia and slag wool for the outer wall(s). tion—Figure 8.9 shows a series of three flat slabs in
& Furnace temperatures are very high compared to the thermal contact with each other.
outside environment, requiring a high-temperature
material for the inner walls that is also expected to DT ¼ DT 1 þ DT 2 þ DT 3 : ð8:12Þ
serve as a structural wall apart from its insulating
properties. Acid or basic bricks are used as refractory & Overall thermal resistance,
bricks depending on the nature of the environments
they come in contact, that is, acidic or alkaline R ¼ R 1 þ R 2 þ R 3 : ð8:13Þ
atmospheres.
& Outer walls serve more as insulating walls to serve q ¼ DT=R ¼ DT 1 =R 1 ¼ DT 2 =R 2 ¼ DT 3 =R 3
much lower temperatures. Outer insulation is pro- ¼ðDT 1 þ DT 2 þ DT 3 Þ=ðR 1 þ R 2 þ R 3 Þ: ð8:14Þ
vided by slag wool or similar insulating material.
. Give expressions for heat conduction through a flat slab & Multilayer hollow cylinder: One-dimensional heat
and hollow cylinder. conduction (Figure 8.10).
& Flat Slab:
q ¼ 2pLðT 1 T 4 Þ=½ln ðr 2 =r 1 Þ=k a þ ln ðr 3 =r 2 Þ=k b
q ¼ kAðt 1 t 2 Þ=Dx; ð8:9Þ þ ln ðr 4 =r 3 Þ=k c : ð8:15Þ
where A is the surface area of the slab, t 1 and t 2 are
temperatures on the two surfaces of the slab, and Dx & In the above equation, contact resistance between the
is the thickness of the slab. adjacent layers is neglected. This is true if the layers
of the composite cylinder are bonded together to
& Hollow Cylinder:
provide intimate contact between adjacent layers,
q ¼ kA L ðt i t o Þ=ðr o r i Þ; ð8:10Þ excluding any air gaps or gaps containing any con-
taminants.Multilayer hollow sphere: One-dimen-
where sional heat conduction ((Figure 8.11).
A ¼ 2pLðr o r i Þ=ln ðr o =r i Þ; ð8:11Þ q ¼ 4pðT 1 T 4 Þ=½ðr 2 r 1 Þ=r 2 r 1 =k a þðr 3 r 2 Þ=
where the subscripts o and i represent outer and inner, r 3 r 2 =k b þðr 4 r 3 Þ=r 4 r 3 =k c : ð8:16Þ
respectively.
. What are heat conduction shape factors?
. When are arithmetic mean and logarithmic mean radii
& Two-dimensional heat transfer in a medium bounded
used in heat conduction to a hollow cylinder?
by two isothermal surfaces at T 1 and T 2 may be
& Arithmetic mean can be used for thin-walled tubes
represented in terms of a conduction shape factor
where the ratio of outer to inner radii is about 1.0.
S (Figure 8.12).
. Write down equations for heat conduction for (i) mul-
tilayer flat wall, (ii) multilayer hollow cylinder, and (iii) q ¼ SkðT 1 T 2 Þ: ð8:17Þ
multilayer hollow sphere.
Multilayer slab.
FIGURE 8.9