Page 254 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 254
DIMENSIONLESS NUMBERS, TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT, AND CONDUCTION HEAT TRANSFER
234
& For most liquids, thermal conductivity decreases & For granular solids, presence of air pockets can cause
with increase in temperature. Simple liquids are more heat transfer not only by the mechanism of conduc-
sensitive than complex liquids such as highly polar tion but also by convection and by radiation from
liquids for which the decrease is slower. surface to surface of the individual particles. This
& k decreases by about 3–4% for a 10 C rise in enhances apparent thermal conductivities by as much
temperature. as 1.5–2.5 times those for the case of still air pockets
in which no convection effects are induced.
& Thermal conductivity for gases increases with
increase in temperature. For monatomic gases, for . What is thermal diffusivity? What is its significance?
1/2
example, it is approximately proportional to T .For & Thermal diffusivity describes the speed of penetra-
small temperature range, k increases nearly linearly tion of heat into the body of a material under applied
with temperature but for wide ranges, the increase is thermal load at its surface.
more rapid than linear increases. & Thermal diffusivity, a, is defined as
& Increase in molecular weight increases k values.
& Gases have very low values of k, as low as 0.007. For heat conducted k 2
a ¼ ¼ m =s: ð8:7Þ
air at 0 C, k is 0.024 W/(m- C). heat stored rc p
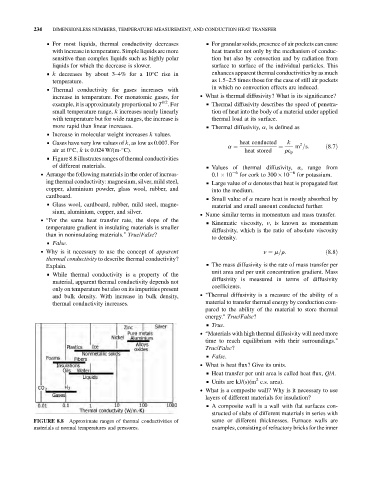
& Figure 8.8 illustrates ranges of thermal conductivities
of different materials. & Values of thermal diffusivity, a, range from
. Arrange the following materials in the order of increas- 0.1 10 6 for cork to 300 10 6 for potassium.
ing thermal conductivity: magnesium, silver, mild steel, & Large value of a denotes that heat is propagated fast
copper, aluminium powder, glass wool, rubber, and into the medium.
cardboard. & Small value of a means heat is mostly absorbed by
& Glass wool, cardboard, rubber, mild steel, magne-
material and small amount conducted further.
sium, aluminium, copper, and silver. . Name similar terms in momentum and mass transfer.
. For the same heat transfer rate, the slope of the
& Kinematic viscosity, n, is known as momentum
temperature gradient in insulating materials is smaller
diffusivity, which is the ratio of absolute viscosity
than in noninsulating materials. True/False?
to density.
& False.
. Why is it necessary to use the concept of apparent n ¼ m=r: ð8:8Þ
thermal conductivity to describe thermal conductivity?
Explain. & The mass diffusivity is the rate of mass transfer per
unit area and per unit concentration gradient. Mass
& While thermal conductivity is a property of the
diffusivity is measured in terms of diffusivity
material, apparent thermal conductivity depends not
coefficients.
only on temperature but also on its impurities present
and bulk density. With increase in bulk density, . Thermal diffusivity is a measure of the ability of a
thermal conductivity increases. material to transfer thermal energy by conduction com-
pared to the ability of the material to store thermal
energy. True/False?
& True.
. Materials with high thermal diffusivity will need more
time to reach equilibrium with their surroundings.
True/False?
& False.
. What is heat flux? Give its units.
& Heat transfer per unit area is called heat flux, Q/A.
2
& Units are kJ/(s)(m c.s. area).
. What is a composite wall? Why is it necessary to use
layers of different materials for insulation?
& A composite wall is a wall with flat surfaces con-
structed of slabs of different materials in series with
Approximate ranges of thermal conductivities of same or different thicknesses. Furnace walls are
FIGURE 8.8
materials at normal temperatures and pressures. examples, consisting of refractory bricks for the inner