Page 252 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 252
DIMENSIONLESS NUMBERS, TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT, AND CONDUCTION HEAT TRANSFER
232
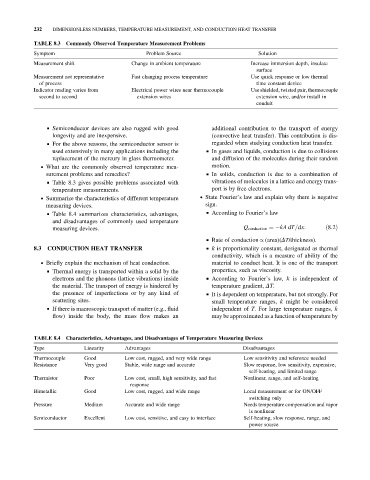
TABLE 8.3 Commonly Observed Temperature Measurement Problems
Symptom Problem Source Solution
Measurement shift Change in ambient temperature Increase immersion depth, insulate
surface
Measurement not representative Fast changing process temperature Use quick response or low thermal
of process time constant device
Indicator reading varies from Electrical power wires near thermocouple Use shielded, twisted pair, thermocouple
second to second extension wires extension wire, and/or install in
conduit
& Semiconductor devices are also rugged with good additional contribution to the transport of energy
longevity and are inexpensive. (convective heat transfer). This contribution is dis-
& For the above reasons, the semiconductor sensor is regarded when studying conduction heat transfer.
used extensively in many applications including the & In gases and liquids, conduction is due to collisions
replacement of the mercury in glass thermometer. and diffusion of the molecules during their random
. What are the commonly observed temperature mea- motion.
surement problems and remedies? & In solids, conduction is due to a combination of
& Table 8.3 gives possible problems associated with vibrations of molecules in a lattice and energy trans-
temperature measurements. port is by free electrons.
. Summarize the characteristics of different temperature . State Fourier’s law and explain why there is negative
measuring devices. sign.
& Table 8.4 summarizes characteristics, advantages, & According to Fourier’s law
and disadvantages of commonly used temperature
measuring devices. Q conduction ¼ kA dT=dx: ð8:2Þ
& Rate of conduction / (area)(DT/thickness).
& k is proportionality constant, designated as thermal
8.3 CONDUCTION HEAT TRANSFER
conductivity, which is a measure of ability of the
. Briefly explain the mechanism of heat conduction. material to conduct heat. It is one of the transport
& Thermal energy is transported within a solid by the properties, such as viscosity.
electrons and the phonons (lattice vibrations) inside & According to Fourier’s law, k is independent of
the material. The transport of energy is hindered by temperature gradient, DT.
the presence of imperfections or by any kind of & It is dependent on temperature, but not strongly. For
scattering sites. small temperature ranges, k might be considered
& If there is macroscopic transport of matter (e.g., fluid independent of T. For large temperature ranges, k
flow) inside the body, the mass flow makes an may be approximated as a function of temperature by
TABLE 8.4 Characteristics, Advantages, and Disadvantages of Temperature Measuring Devices
Type Linearity Advantages Disadvantages
Thermocouple Good Low cost, rugged, and very wide range Low sensitivity and reference needed
Resistance Very good Stable, wide range and accurate Slow response, low sensitivity, expensive,
self-heating, and limited range
Thermistor Poor Low cost, small, high sensitivity, and fast Nonlinear, range, and self-heating
response
Bimetallic Good Low cost, rugged, and wide range Local measurement or for ON/OFF
switching only
Pressure Medium Accurate and wide range Needs temperature compensation and vapor
is nonlinear
Semiconductor Excellent Low cost, sensitive, and easy to interface Self-heating, slow response, range, and
power source