Page 477 - Forensic Structural Engineering Handbook
P. 477
13.22 MATERIAL-SPECIFIC FORENSIC ANALYSES
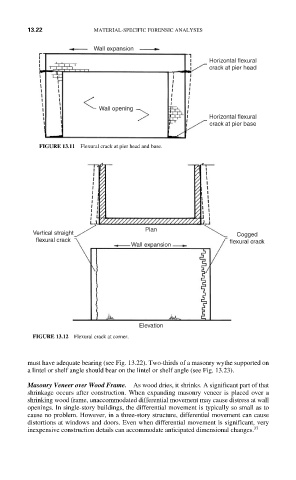
Wall expansion
Horizontal flexural
crack at pier head
Wall opening
Horizontal flexural
crack at pier base
FIGURE 13.11 Flexural crack at pier head and base.
Plan
Vertical straight Cogged
flexural crack flexural crack
Wall expansion
Elevation
FIGURE 13.12 Flexural crack at corner.
must have adequate bearing (see Fig. 13.22). Two-thirds of a masonry wythe supported on
a lintel or shelf angle should bear on the lintel or shelf angle (see Fig. 13.23).
Masonry Veneer over Wood Frame. As wood dries, it shrinks. A significant part of that
shrinkage occurs after construction. When expanding masonry veneer is placed over a
shrinking wood frame, unaccommodated differential movement may cause distress at wall
openings. In single-story buildings, the differential movement is typically so small as to
cause no problem. However, in a three-story structure, differential movement can cause
distortions at windows and doors. Even when differential movement is significant, very
inexpensive construction details can accommodate anticipated dimensional changes. 37