Page 258 - Formation Damage during Improved Oil Recovery Fundamentals and Applications
P. 258
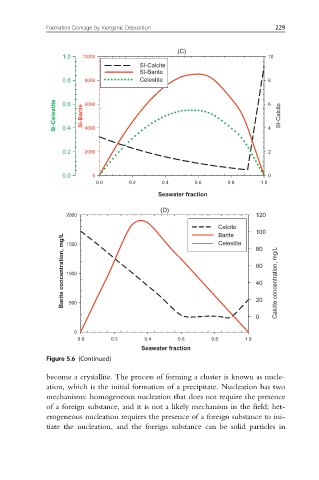
Formation Damage by Inorganic Deposition 229
(C)
1.0 10000 10
SI-Calcite
SI-Barite
0.8 8000 Celestite 8
Si-Celestite 0.6 Si-Barite 6000 6 4 SI-Calcite
4000
0.4
0.2 2000 2
0.0 0 0
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
Seawater fraction
(D)
2000 120
Calcite
100
Barite
Barite concentration, mg/L 1000 60 Calcite concentration, mg/L
Celestite
1500
80
40
500
0 20
0
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
Seawater fraction
Figure 5.6 (Continued)
become a crystallite. The process of forming a cluster is known as nucle-
ation, which is the initial formation of a precipitate. Nucleation has two
mechanisms: homogeneous nucleation that does not require the presence
of a foreign substance, and it is not a likely mechanism in the field; het-
erogeneous nucleation requires the presence of a foreign substance to ini-
tiate the nucleation, and the foreign substance can be solid particles in