Page 548 - Subyek Teknik Mesin - Forsthoffers Best Practice Handbook for Rotating Machinery by William E Forsthoffer
P. 548
Dry Gas Seal Best Practices Be st Practice 9.8
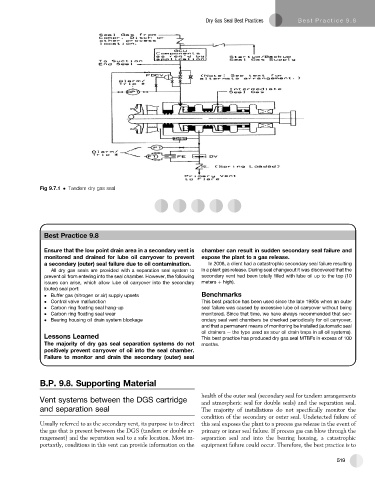
Fig 9.7.1 Tandem dry gas seal
Best
Best Practice 9.8Practice 9.8
Ensure that the low point drain area in a secondary vent is chamber can result in sudden secondary seal failure and
monitored and drained for lube oil carryover to prevent expose the plant to a gas release.
a secondary (outer) seal failure due to oil contamination. In 2008, a client had a catastrophic secondary seal failure resulting
All dry gas seals are provided with a separation seal system to in a plant gas release. During seal changeout it was discovered that the
prevent oil from entering into the seal chamber. However, the following secondary vent had been totally filled with lube oil up to the top (10
issues can arise, which allow lube oil carryover into the secondary meters þ high).
(outer) seal port:
Buffer gas (nitrogen or air) supply upsets Benchmarks
Control valve malfunction This best practice has been used since the late 1990s when an outer
Carbon ring floating seal hang-up seal failure was caused by excessive lube oil carryover without being
Carbon ring floating seal wear monitored. Since that time, we have always recommended that sec-
Bearing housing oil drain system blockage ondary seal vent chambers be checked periodically for oil carryover,
and that a permanent means of monitoring be installed (automatic seal
oil drainers e the type used as sour oil drain traps in all oil systems).
Lessons Learned This best practice has produced dry gas seal MTBFs in excess of 100
The majority of dry gas seal separation systems do not months.
positively prevent carryover of oil into the seal chamber.
Failure to monitor and drain the secondary (outer) seal
B.P. 9.8. Supporting Material
health of the outer seal (secondary seal for tandem arrangements
Vent systems between the DGS cartridge and atmospheric seal for double seals) and the separation seal.
and separation seal The majority of installations do not specifically monitor the
condition of the secondary or outer seal. Undetected failure of
Usually referred to as the secondary vent, its purpose is to direct this seal exposes the plant to a process gas release in the event of
the gas that is present between the DGS (tandem or double ar- primary or inner seal failure. If process gas can blow through the
rangement) and the separation seal to a safe location. Most im- separation seal and into the bearing housing, a catastrophic
portantly, conditions in this vent can provide information on the equipment failure could occur. Therefore, the best practice is to
519