Page 266 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 266
Cognitive radio based smart grid communications Chapter 6 237
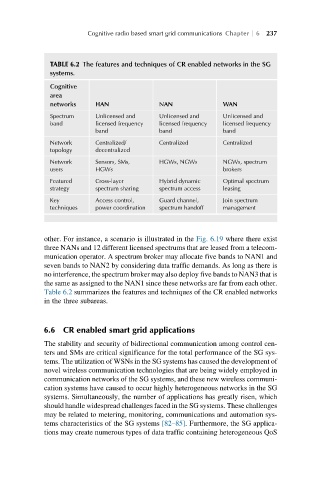
TABLE 6.2 The features and techniques of CR enabled networks in the SG
systems.
Cognitive
area
networks HAN NAN WAN
Spectrum Unlicensed and Unlicensed and Unlicensed and
band licensed frequency licensed frequency licensed frequency
band band band
Network Centralized/ Centralized Centralized
topology decentralized
Network Sensors, SMs, HGWs, NGWs NGWs, spectrum
users HGWs brokers
Featured Cross-layer Hybrid dynamic Optimal spectrum
strategy spectrum sharing spectrum access leasing
Key Access control, Guard channel, Join spectrum
techniques power coordination spectrum handoff management
other. For instance, a scenario is illustrated in the Fig. 6.19 where there exist
three NANs and 12 different licensed spectrums that are leased from a telecom-
munication operator. A spectrum broker may allocate five bands to NAN1 and
seven bands to NAN2 by considering data traffic demands. As long as there is
no interference, the spectrum broker may also deploy five bands to NAN3 that is
the same as assigned to the NAN1 since these networks are far from each other.
Table 6.2 summarizes the features and techniques of the CR enabled networks
in the three subareas.
6.6 CR enabled smart grid applications
The stability and security of bidirectional communication among control cen-
ters and SMs are critical significance for the total performance of the SG sys-
tems. The utilization of WSNs in the SG systems has caused the development of
novel wireless communication technologies that are being widely employed in
communication networks of the SG systems, and these new wireless communi-
cation systems have caused to occur highly heterogeneous networks in the SG
systems. Simultaneously, the number of applications has greatly risen, which
should handle widespread challenges faced in the SG systems. These challenges
may be related to metering, monitoring, communications and automation sys-
tems characteristics of the SG systems [82–85]. Furthermore, the SG applica-
tions may create numerous types of data traffic containing heterogeneous QoS