Page 263 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 263
234 From smart grid to internet of energy
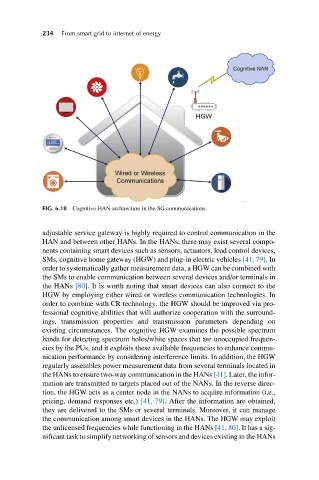
FIG. 6.18 Cognitive HAN architecture in the SG communications.
adjustable service gateway is highly required to control communication in the
HAN and between other HANs. In the HANs, there may exist several compo-
nents containing smart devices such as sensors, actuators, load control devices,
SMs, cognitive home gateway (HGW) and plug-in electric vehicles [41, 79].In
order to systematically gather measurement data, a HGW can be combined with
the SMs to enable communication between several devices and/or terminals in
the HANs [80]. It is worth noting that smart devices can also connect to the
HGW by employing either wired or wireless communication technologies. In
order to combine with CR technology, the HGW should be improved via pro-
fessional cognitive abilities that will authorize cooperation with the surround-
ings, transmission properties and transmission parameters depending on
existing circumstances. The cognitive HGW examines the possible spectrum
bands for detecting spectrum holes/white spaces that are unoccupied frequen-
cies by the PUs, and it exploits these available frequencies to enhance commu-
nication performance by considering interference limits. In addition, the HGW
regularly assembles power measurement data from several terminals located in
the HANs to ensure two-way communication in the HANs [41]. Later, the infor-
mation are transmitted to targets placed out of the NANs. In the reverse direc-
tion, the HGW acts as a center node in the NANs to acquire information (i.e.,
pricing, demand responses etc.) [41, 79]. After the information are obtained,
they are delivered to the SMs or several terminals. Moreover, it can manage
the communication among smart devices in the HANs. The HGW may exploit
the unlicensed frequencies while functioning in the HANs [41, 80]. It has a sig-
nificant task to simplify networking of sensors and devices existing in the HANs