Page 258 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 258
230 From smart grid to internet of energy
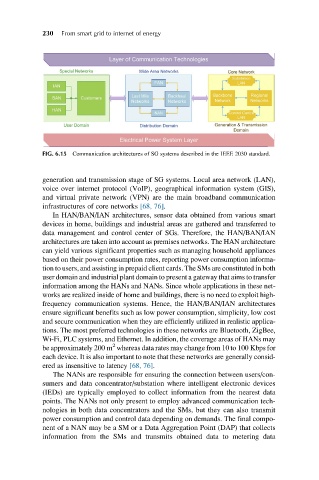
FIG. 6.15 Communication architectures of SG systems described in the IEEE 2030 standard.
generation and transmission stage of SG systems. Local area network (LAN),
voice over internet protocol (VoIP), geographical information system (GIS),
and virtual private network (VPN) are the main broadband communication
infrastructures of core networks [68, 76].
In HAN/BAN/IAN architectures, sensor data obtained from various smart
devices in home, buildings and industrial areas are gathered and transferred to
data management and control center of SGs. Therefore, the HAN/BAN/IAN
architectures are taken into account as premises networks. The HAN architecture
can yield various significant properties such as managing household appliances
based on their power consumption rates, reporting power consumption informa-
tion to users, and assisting in prepaid client cards. The SMs are constituted in both
user domain and industrial plant domain to present a gateway that aims to transfer
information among the HANs and NANs. Since whole applications in these net-
works are realized inside of home and buildings, there is no need to exploit high-
frequency communication systems. Hence, the HAN/BAN/IAN architectures
ensure significant benefits such as low power consumption, simplicity, low cost
and secure communication when they are efficiently utilized in realistic applica-
tions. The most preferred technologies in these networks are Bluetooth, ZigBee,
Wi-Fi, PLC systems, and Ethernet. In addition, the coverage areas of HANs may
2
be approximately 200 m whereas data rates may change from 10 to 100 Kbps for
each device. It is also important to note that these networks are generally consid-
ered as insensitive to latency [68, 76].
The NANs are responsible for ensuring the connection between users/con-
sumers and data concentrator/substation where intelligent electronic devices
(IEDs) are typically employed to collect information from the nearest data
points. The NANs not only present to employ advanced communication tech-
nologies in both data concentrators and the SMs, but they can also transmit
power consumption and control data depending on demands. The final compo-
nent of a NAN may be a SM or a Data Aggregation Point (DAP) that collects
information from the SMs and transmits obtained data to metering data