Page 259 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 259
Cognitive radio based smart grid communications Chapter 6 231
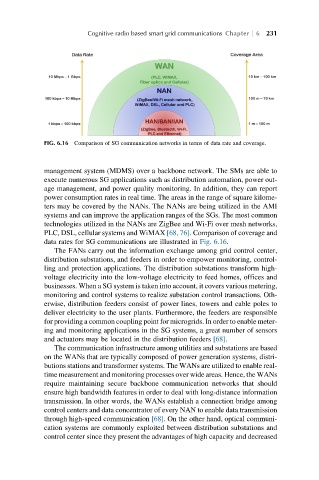
FIG. 6.16 Comparison of SG communication networks in terms of data rate and coverage.
management system (MDMS) over a backbone network. The SMs are able to
execute numerous SG applications such as distribution automation, power out-
age management, and power quality monitoring. In addition, they can report
power consumption rates in real time. The areas in the range of square kilome-
ters may be covered by the NANs. The NANs are being utilized in the AMI
systems and can improve the application ranges of the SGs. The most common
technologies utilized in the NANs are ZigBee and Wi-Fi over mesh networks,
PLC, DSL, cellular systems and WiMAX [68, 76]. Comparison of coverage and
data rates for SG communications are illustrated in Fig. 6.16.
The FANs carry out the information exchange among grid control center,
distribution substations, and feeders in order to empower monitoring, control-
ling and protection applications. The distribution substations transform high-
voltage electricity into the low-voltage electricity to feed homes, offices and
businesses. When a SG system is taken into account, it covers various metering,
monitoring and control systems to realize substation control transactions. Oth-
erwise, distribution feeders consist of power lines, towers and cable poles to
deliver electricity to the user plants. Furthermore, the feeders are responsible
for providing a common coupling point for microgrids. In order to enable meter-
ing and monitoring applications in the SG systems, a great number of sensors
and actuators may be located in the distribution feeders [68].
The communication infrastructure among utilities and substations are based
on the WANs that are typically composed of power generation systems, distri-
butions stations and transformer systems. The WANs are utilized to enable real-
time measurement and monitoring processes over wide areas. Hence, the WANs
require maintaining secure backbone communication networks that should
ensure high bandwidth features in order to deal with long-distance information
transmission. In other words, the WANs establish a connection bridge among
control centers and data concentrator of every NAN to enable data transmission
through high-speed communication [68]. On the other hand, optical communi-
cation systems are commonly exploited between distribution substations and
control center since they present the advantages of high capacity and decreased