Page 280 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 280
Internet of things for smart grid applications Chapter 7 251
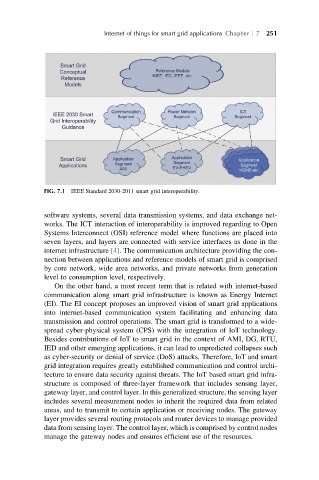
FIG. 7.1 IEEE Standard 2030-2011 smart grid interoperability.
software systems, several data transmission systems, and data exchange net-
works. The ICT interaction of interoperability is improved regarding to Open
Systems Interconnect (OSI) reference model where functions are placed into
seven layers, and layers are connected with service interfaces as done in the
internet infrastructure [4]. The communication architecture providing the con-
nection between applications and reference models of smart grid is comprised
by core network, wide area networks, and private networks from generation
level to consumption level, respectively.
On the other hand, a most recent term that is related with internet-based
communication along smart grid infrastructure is known as Energy Internet
(EI). The EI concept proposes an improved vision of smart grid applications
into internet-based communication system facilitating and enhancing data
transmission and control operations. The smart grid is transformed to a wide-
spread cyber-physical system (CPS) with the integration of IoT technology.
Besides contributions of IoT to smart grid in the context of AMI, DG, RTU,
IED and other emerging applications, it can lead to unpredicted collapses such
as cyber-security or denial of service (DoS) attacks. Therefore, IoT and smart
grid integration requires greatly established communication and control archi-
tecture to ensure data security against threats. The IoT based smart grid infra-
structure is composed of three-layer framework that includes sensing layer,
gateway layer, and control layer. In this generalized structure, the sensing layer
includes several measurement nodes to inherit the required data from related
areas, and to transmit to certain application or receiving nodes. The gateway
layer provides several routing protocols and router devices to manage provided
data from sensing layer. The control layer, which is comprised by control nodes
manage the gateway nodes and ensures efficient use of the resources.