Page 355 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 355
Big data, privacy and security in smart grids Chapter 8 319
8.3 Big data analysis methods
The big data analytics define all processes and procedures for discovering the
required data from databases by using particular methods, tools, and analyses.
The amount of acquired data is gradually increasing due to spreading use of big
data infrastructures, and improves the requirements of obtaining true data
among stacks. One of the most important challenge in Big Data analytics is
transforming relevant data to predicted outcomes and making the possible most
appropriate decision. The fundamental hindrances are related by noisy, incor-
rect, and biased structure of obtained data. Therefore, the quality of data ana-
lytics is directly related with quality of the data. The reliability can be classified
regarding to used data quality metrics that can provide information on how user
data are precise. The evaluation of acquired data and data quality is the first step
of detecting data extraction from massive stacks. The evaluation criteria should
include accuracy, reliability, completeness, and firmness since each of these
provide assessment information about structured databases. Ardagna et al. pro-
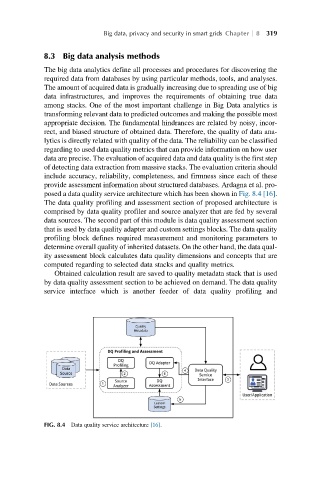
posed a data quality service architecture which has been shown in Fig. 8.4 [16].
The data quality profiling and assessment section of proposed architecture is
comprised by data quality profiler and source analyzer that are fed by several
data sources. The second part of this module is data quality assessment section
that is used by data quality adapter and custom settings blocks. The data quality
profiling block defines required measurement and monitoring parameters to
determine overall quality of inherited datasets. On the other hand, the data qual-
ity assessment block calculates data quality dimensions and concepts that are
computed regarding to selected data stacks and quality metrics.
Obtained calculation result are saved to quality metadata stack that is used
by data quality assessment section to be achieved on demand. The data quality
service interface which is another feeder of data quality profiling and
FIG. 8.4 Data quality service architecture [16].