Page 357 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 357
Big data, privacy and security in smart grids Chapter 8 321
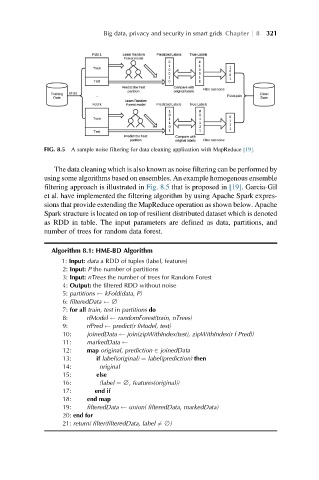
FIG. 8.5 A sample noise filtering for data cleaning application with MapReduce [19].
The data cleaning which is also known as noise filtering can be performed by
using some algorithms based on ensembles. An example homogenous ensemble
filtering approach is illustrated in Fig. 8.5 that is proposed in [19]. Garcia-Gil
et al. have implemented the filtering algorithm by using Apache Spark expres-
sions that provide extending the MapReduce operation as shown below. Apache
Spark structure is located on top of resilient distributed dataset which is denoted
as RDD in table. The input parameters are defined as data, partitions, and
number of trees for random data forest.
Algorithm 8.1: HME-BD Algorithm
1: Input: data a RDD of tuples (label, features)
2: Input: P the number of partitions
3: Input: nTrees the number of trees for Random Forest
4: Output: the filtered RDD without noise
5: partitions kFold(data, P)
6: filteredData ∅
7: for all train, test in partitions do
8: rfModel randomForest(train, nTrees)
9: rfPred predict(r fModel, test)
10: joinedData join(zipWithIndex(test), zipWithIndex(r f Pred))
11: markedData
12: map original, prediction 2 joinedData
13: if label(original) ¼ label(prediction) then
14: original
15: else
16: (label ¼ ∅, features(original))
17: end if
18: end map
19: filteredData union( filteredData, markedData)
20: end for
21: return( filter(filteredData, label 6¼ ∅)