Page 43 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 43
32 From smart grid to internet of energy
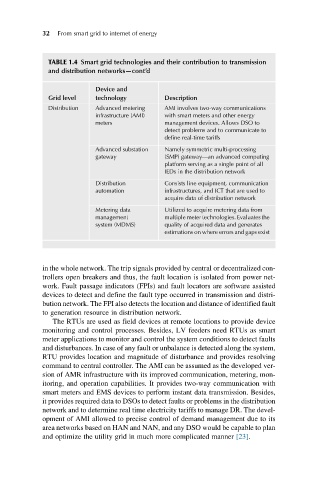
TABLE 1.4 Smart grid technologies and their contribution to transmission
and distribution networks—cont’d
Device and
Grid level technology Description
Distribution Advanced metering AMI involves two-way communications
infrastructure (AMI) with smart meters and other energy
meters management devices. Allows DSO to
detect problems and to communicate to
define real-time tariffs
Advanced substation Namely symmetric multi-processing
gateway (SMP) gateway—an advanced computing
platform serving as a single point of all
IEDs in the distribution network
Distribution Consists line equipment, communication
automation infrastructures, and ICT that are used to
acquire data of distribution network
Metering data Utilized to acquire metering data from
management multiple meter technologies. Evaluates the
system (MDMS) quality of acquired data and generates
estimations on where errors and gaps exist
in the whole network. The trip signals provided by central or decentralized con-
trollers open breakers and thus, the fault location is isolated from power net-
work. Fault passage indicators (FPIs) and fault locators are software assisted
devices to detect and define the fault type occurred in transmission and distri-
bution network. The FPI also detects the location and distance of identified fault
to generation resource in distribution network.
The RTUs are used as field devices at remote locations to provide device
monitoring and control processes. Besides, LV feeders need RTUs as smart
meter applications to monitor and control the system conditions to detect faults
and disturbances. In case of any fault or unbalance is detected along the system,
RTU provides location and magnitude of disturbance and provides resolving
command to central controller. The AMI can be assumed as the developed ver-
sion of AMR infrastructure with its improved communication, metering, mon-
itoring, and operation capabilities. It provides two-way communication with
smart meters and EMS devices to perform instant data transmission. Besides,
it provides required data to DSOs to detect faults or problems in the distribution
network and to determine real time electricity tariffs to manage DR. The devel-
opment of AMI allowed to precise control of demand management due to its
area networks based on HAN and NAN, and any DSO would be capable to plan
and optimize the utility grid in much more complicated manner [23].