Page 42 - From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy
P. 42
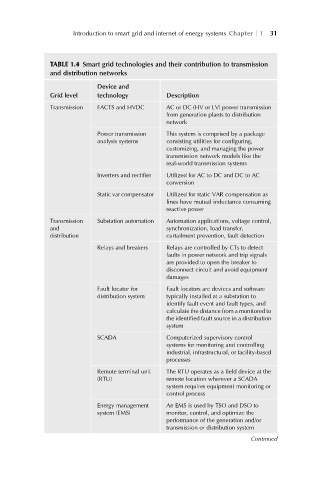
Introduction to smart grid and internet of energy systems Chapter 1 31
TABLE 1.4 Smart grid technologies and their contribution to transmission
and distribution networks
Device and
Grid level technology Description
Transmission FACTS and HVDC AC or DC (HV or LV) power transmission
from generation plants to distribution
network
Power transmission This system is comprised by a package
analysis systems consisting utilities for configuring,
customizing, and managing the power
transmission network models like the
real-world transmission systems
Inverters and rectifier Utilized for AC to DC and DC to AC
conversion
Static var compensator Utilized for static VAR compensation as
lines have mutual inductance consuming
reactive power
Transmission Substation automation Automation applications, voltage control,
and synchronization, load transfer,
distribution curtailment prevention, fault detection
Relays and breakers Relays are controlled by CTs to detect
faults in power network and trip signals
are provided to open the breaker to
disconnect circuit and avoid equipment
damages
Fault locator for Fault locators are devices and software
distribution system typically installed at a substation to
identify fault event and fault types, and
calculate the distance from a monitored to
the identified fault source in a distribution
system
SCADA Computerized supervisory control
systems for monitoring and controlling
industrial, infrastructural, or facility-based
processes
Remote terminal unit The RTU operates as a field device at the
(RTU) remote location wherever a SCADA
system requires equipment monitoring or
control process
Energy management An EMS is used by TSO and DSO to
system (EMS) monitor, control, and optimize the
performance of the generation and/or
transmission or distribution system
Continued