Page 419 - Fundamentals of Air Pollution 3E
P. 419
II. Conversion of Effects Data and Criteria to Standards 371
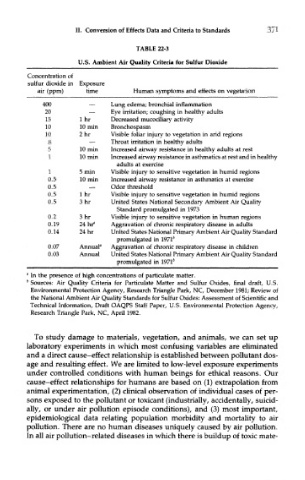
TABLE 22-3
U.S. Ambient Air Quality Criteria for Sulfur Dioxide
Concentration of
sulfur dioxide in Exposure
air (ppm) time Human symptoms and effects on vegetation
400 — Lung edema; bronchial inflammation
20 — Eye irritation; coughing in healthy adults
15 Ihr Decreased mucociliary activity
10 10 min Bronchospasm
10 2hr Visible foliar injury to vegetation in arid regions
8 — Throat irritation in healthy adults
5 10 min Increased airway resistance in healthy adults at rest
1 10 min Increased airway resistance in asthmatics at rest and in healthy
adults at exercise
1 5 min Visible injury to sensitive vegetation in humid regions
0.5 10 min Increased airway resistance in asthmatics at exercise
0.5 — Odor threshold
0.5 1 hr Visible injury to sensitive vegetation in humid regions
0.5 3hr United States National Secondary Ambient Air Quality
Standard promulgated in 1973
0.2 3hr Visible injury to sensitive vegetation in human regions
0.19 24 hf Aggravation of chronic respiratory disease in adults
0.14 24 hr United States National Primary Ambient Air Quality Standard
promulgated in 1971 *
0.07 Annual" Aggravation of chronic respiratory disease in children
0.03 Annual United States National Primary Ambient Air Quality Standard
promulgated in I971 b
" In the presence of high concentrations of particulate matter.
b
Sources: Air Quality Criteria for Particulate Matter and Sulfur Oxides, final draft, U.S.
Environmental Protection Agency, Research Triangle Park, NC, December 1981; Review of
the National Ambient Air Quality Standards for Sulfur Oxides: Assessment of Scientific and
Technical Information, Draft OAQPS Staff Paper, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency,
Research Triangle Park, NC, April 1982.
To study damage to materials, vegetation, and animals, we can set up
laboratory experiments in which most confusing variables are eliminated
and a direct cause-effect relationship is established between pollutant dos-
age and resulting effect. We are limited to low-level exposure experiments
under controlled conditions with human beings for ethical reasons. Our
cause-effect relationships for humans are based on (1) extrapolation from
animal experimentation, (2) clinical observation of individual cases of per-
sons exposed to the pollutant or toxicant (industrially, accidentally, suicid-
ally, or under air pollution episode conditions), and (3) most important,
epidemiological data relating population morbidity and mortality to air
pollution. There are no human diseases uniquely caused by air pollution.
In all air pollution-related diseases in which there is buildup of toxic mate-