Page 17 - Fundamentals of Enhanced Oil and Gas Recovery
P. 17
An Introduction to Enhanced Oil Recovery 5
σ ow
Oil
Oil Water
α
σ
σ
os
ws Solid
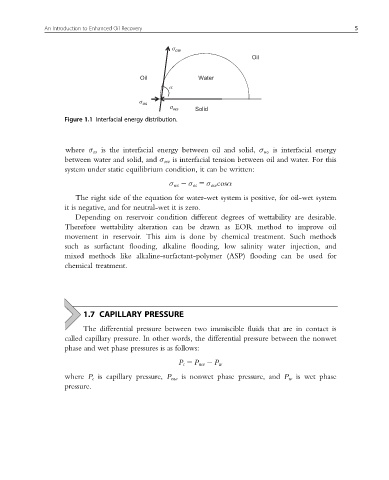
Figure 1.1 Interfacial energy distribution.
where σ os is the interfacial energy between oil and solid, σ ws is interfacial energy
between water and solid, and σ ow is interfacial tension between oil and water. For this
system under static equilibrium condition, it can be written:
σ ws 2 σ os 5 σ ow cosα
The right side of the equation for water-wet system is positive, for oil-wet system
it is negative, and for neutral-wet it is zero.
Depending on reservoir condition different degrees of wettability are desirable.
Therefore wettability alteration can be drawn as EOR method to improve oil
movement in reservoir. This aim is done by chemical treatment. Such methods
such as surfactant flooding, alkaline flooding, low salinity water injection, and
mixed methods like alkaline-surfactant-polymer (ASP) flooding can be used for
chemical treatment.
1.7 CAPILLARY PRESSURE
The differential pressure between two immiscible fluids that are in contact is
called capillary pressure. In other words, the differential pressure between the nonwet
phase and wet phase pressures is as follows:
P c 5 P nw 2 P w
where P c is capillary pressure, P nw is nonwet phase pressure, and P w is wet phase
pressure.