Page 18 - Fundamentals of Enhanced Oil and Gas Recovery
P. 18
6 Amirhossein Mohammadi Alamooti and Farzan Karimi Malekabadi
σ
Phase 2 P 2
1
P
Phase 1
r
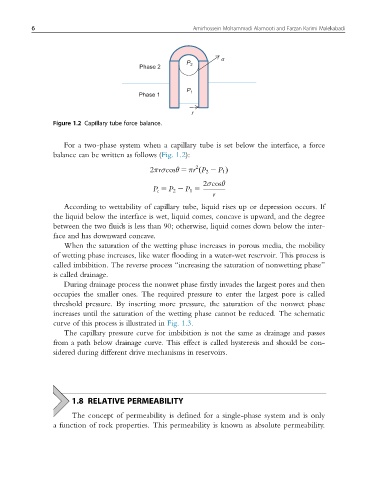
Figure 1.2 Capillary tube force balance.
For a two-phase system when a capillary tube is set below the interface, a force
balance can be written as follows (Fig. 1.2):
2
2πrσcosθ 5 πr P 2 2 P 1 Þ
ð
2σcosθ
P c 5 P 2 2 P 1 5
r
According to wettability of capillary tube, liquid rises up or depression occurs. If
the liquid below the interface is wet, liquid comes, concave is upward, and the degree
between the two fluids is less than 90; otherwise, liquid comes down below the inter-
face and has downward concave.
When the saturation of the wetting phase increases in porous media, the mobility
of wetting phase increases, like water flooding in a water-wet reservoir. This process is
called imbibition. The reverse process “increasing the saturation of nonwetting phase”
is called drainage.
During drainage process the nonwet phase firstly invades the largest pores and then
occupies the smaller ones. The required pressure to enter the largest pore is called
threshold pressure. By inserting more pressure, the saturation of the nonwet phase
increases until the saturation of the wetting phase cannot be reduced. The schematic
curve of this process is illustrated in Fig. 1.3.
The capillary pressure curve for imbibition is not the same as drainage and passes
from a path below drainage curve. This effect is called hysteresis and should be con-
sidered during different drive mechanisms in reservoirs.
1.8 RELATIVE PERMEABILITY
The concept of permeability is defined for a single-phase system and is only
a function of rock properties. This permeability is known as absolute permeability.