Page 314 - Fundamentals of Gas Shale Reservoirs
P. 314
294 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF UNCONVENTIONAL SHALE RESERVOIRS
Logarithmic
gridding
Hydraulic h
fracture
Matrix
blocks
L y
L x
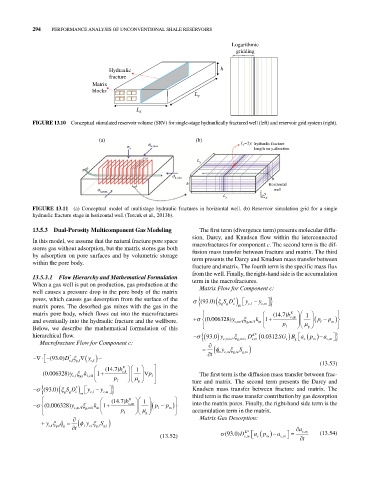
FIgURE 13.10 Conceptual stimulated reservoir volume (SRV) for single‐stage hydraulically fractured well (left) and reservoir grid system (right).
(a) (b)
L t =2y: hydraulic fracture
v h,max length on y-direction
L y
h,min
h Horizontal
h,max z well
y
L x x
FIgURE 13.11 (a) Conceptual model of multistage hydraulic fractures in horizontal well. (b) Reservoir simulation grid for a single
hydraulic fracture stage in horizontal well (Torcuk et al., 2013b).
13.5.3 Dual-Porosity Multicomponent gas Modeling The first term (divergence term) presents molecular diffu-
sion, Darcy, and Knudsen flow within the interconnected
In this model, we assume that the natural fracture pore space macrofractures for component c. The second term is the dif-
stores gas without adsorption, but the matrix stores gas both fusion mass transfer between fracture and matrix. The third
by adsorption on pore surfaces and by volumetric storage term presents the Darcy and Knudsen mass transfer between
within the pore body.
fracture and matrix. The fourth term is the specific mass flux
from the well. Finally, the right‐hand side is the accumulation
13.5.3.1 Flow Hierarchy and Mathematical Formulation term in the macrofractures.
When a gas well is put on production, gas production at the Matrix Flow for Component c:
well causes a pressure drop in the pore body of the matrix
pores, which causes gas desorption from the surface of the (93 . ) SD * y y
0
matrix pores. The desorbed gas mixes with the gas in the g g c m , cf , cm
matrix pore body, which flows out into the macrofractures (. K , cm 1
14 7)b
k
0
and eventually into the hydraulic fracture and the wellbore. (.006328 )y cm g mf m 1 1 p p f p m
,/f
,/
Below, we describe the mathematical formulation of this f g
hierarchical flow. 93 0 . y cm s , g ms D K* . 0 0312 SG Ba c p m a cm
,
g
s
,
,/
,/
cm
Macrofracture Flow for Component c:
y y S
,
t m cm gm, , gm
(93.0)D * y
c,f g,f c,f
(13.53)
(14.7)b K 1
(0.006328)y k 1 c,f p The first term is the diffusion mass transfer between frac-
c,f g,f f,eff f
p
f g ture and matrix. The second term presents the Darcy and
(93.0) SD * y y Knudsen mass transfer between fracture and matrix. The
c
g g
m c,f c,m third term is the mass transfer contribution by gas desorption
(14.7)b K 1
(0.006328)y k 1 c,m p p into the matrix pores. Finally, the right‐hand side term is the
c,m/f g,m/f m f m
p f g accumulation term in the matrix.
Matrix Gas Desorption:
y ˆ q y S
c,f g,f g
t f c,f g,f g,f K * a , cm
0
(13.52) (93 . )D , cm a c p m a , cm (13.54)
t