Page 312 - Fundamentals of Gas Shale Reservoirs
P. 312
292 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF UNCONVENTIONAL SHALE RESERVOIRS
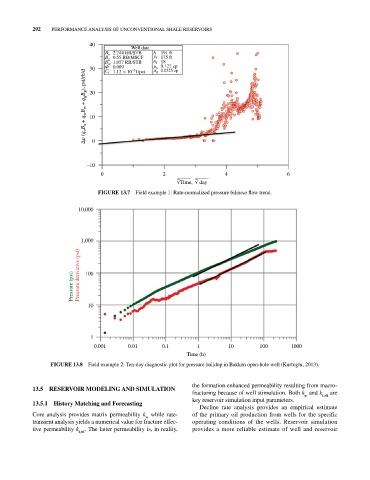
40
Well data
B o 2.744 RB/STB h y 191 ft
B g 0.55 RB/MSCF f 175 ft
B w 1.057 RB/STB n f 18
30 t 0.089 –5 o g 0.127 cp
0.0325 cp
C
p (q o B o + q w B w + q g B g ), psi/rb/d 20
1.12 × 10 1/psi
10
–10 0
0 2 4 6
4 √ Time, √ day
4
FIgURE 13.7 Field example 1: Rate‐normalized pressure bilinear flow trend.
10,000
1,000
Pressure (psi) Pressure derivative (psi) 100
10
1
0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1000
Time (h)
FIgURE 13.8 Field example 2: Ten‐day diagnostic plot for pressure buildup in Bakken open‐hole well (Kurtoglu, 2013).
the formation enhanced permeability resulting from macro-
13.5 RESERVOIR MODELINg AND SIMULATION
fracturing because of well stimulation. Both k and k are
m
f,eff
key reservoir simulation input parameters.
13.5.1 History Matching and Forecasting
Decline rate analysis provides an empirical estimate
Core analysis provides matrix permeability k while rate‐ of the primary oil production from wells for the specific
m
transient analysis yields a numerical value for fracture effec- operating conditions of the wells. Reservoir simulation
tive permeability k . The latter permeability is, in reality, provides a more reliable estimate of well and reservoir
f,eff