Page 140 - Fundamentals of Geomorphology
P. 140
SMALL-SCALE TECTONIC AND STRUCTURAL LANDFORMS 123
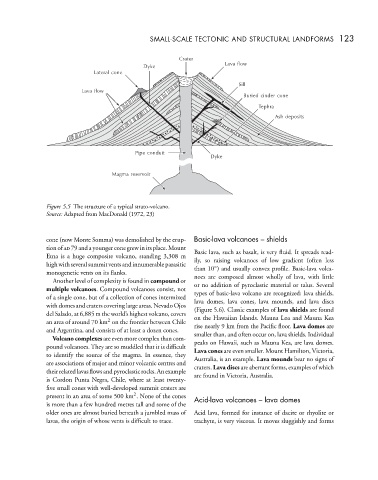
Crater
Lava flow
Dyke
Lateral cone
Sill
Lava flow
Buried cinder cone
Tephra
Ash deposits
Pipe conduit
Dyke
Magma reservoir
Figure 5.5 The structure of a typical strato-volcano.
Source: Adapted from MacDonald (1972, 23)
cone (now Monte Somma) was demolished by the erup- Basic-lava volcanoes – shields
tion of AD 79 and a younger cone grew in its place. Mount Basic lava, such as basalt, is very fluid. It spreads read-
Etna is a huge composite volcano, standing 3,308 m ily, so raising volcanoes of low gradient (often less
highwithseveralsummitventsandinnumerableparasitic than 10 ) and usually convex profile. Basic-lava volca-
◦
monogenetic vents on its flanks. noes are composed almost wholly of lava, with little
Another level of complexity is found in compound or
multiple volcanoes. Compound volcanoes consist, not or no addition of pyroclastic material or talus. Several
types of basic-lava volcano are recognized: lava shields,
of a single cone, but of a collection of cones intermixed lava domes, lava cones, lava mounds, and lava discs
with domes and craters covering large areas. Nevado Ojos (Figure 5.6). Classic examples of lava shields are found
del Salado, at 6,885 m the world’s highest volcano, covers on the Hawaiian Islands. Mauna Loa and Mauna Kea
2
an area of around 70 km on the frontier between Chile
and Argentina, and consists of at least a dozen cones. rise nearly 9 km from the Pacific floor. Lava domes are
smaller than, and often occur on, lava shields. Individual
Volcano complexes are even more complex than com-
pound volcanoes. They are so muddled that it is difficult peaks on Hawaii, such as Mauna Kea, are lava domes.
Lava cones are even smaller. Mount Hamilton, Victoria,
to identify the source of the magma. In essence, they Australia, is an example. Lava mounds bear no signs of
are associations of major and minor volcanic centres and craters. Lava discs are aberrant forms, examples of which
theirrelatedlavasflowsandpyroclasticrocks.Anexample are found in Victoria, Australia.
is Cordon Punta Negra, Chile, where at least twenty-
five small cones with well-developed summit craters are
2
present in an area of some 500 km . None of the cones Acid-lava volcanoes – lava domes
is more than a few hundred metres tall and some of the
older ones are almost buried beneath a jumbled mass of Acid lava, formed for instance of dacite or rhyolite or
lavas, the origin of whose vents is difficult to trace. trachyte, is very viscous. It moves sluggishly and forms