Page 48 - Fundamentals of Light Microscopy and Electronic Imaging
P. 48
ILLUMINATORS AND THEIR SPECTRA 31
366 Mercury
435
405
546
578
300 400 500 600 700
(a)
Relative intensity Xenon
400 600 800 1000 1200
(b)
3400K Halogen
3000K
2600K
2200K
500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000
Wavelength (nm)
(c)
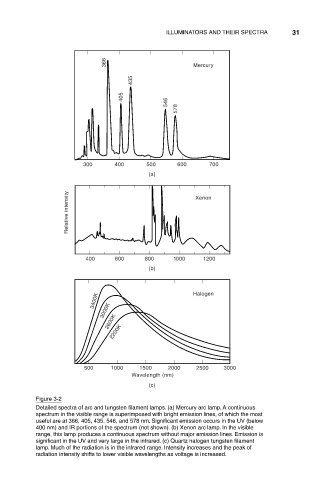
Figure 3-2
Detailed spectra of arc and tungsten filament lamps. (a) Mercury arc lamp. A continuous
spectrum in the visible range is superimposed with bright emission lines, of which the most
useful are at 366, 405, 435, 546, and 578 nm. Significant emission occurs in the UV (below
400 nm) and IR portions of the spectrum (not shown). (b) Xenon arc lamp. In the visible
range, this lamp produces a continuous spectrum without major emission lines. Emission is
significant in the UV and very large in the infrared. (c) Quartz halogen tungsten filament
lamp. Much of the radiation is in the infrared range. Intensity increases and the peak of
radiation intensity shifts to lower visible wavelengths as voltage is increased.