Page 321 - Fundamentals of Magnetic Thermonuclear Reactor Design
P. 321
300 Fundamentals of Magnetic Thermonuclear Reactor Design
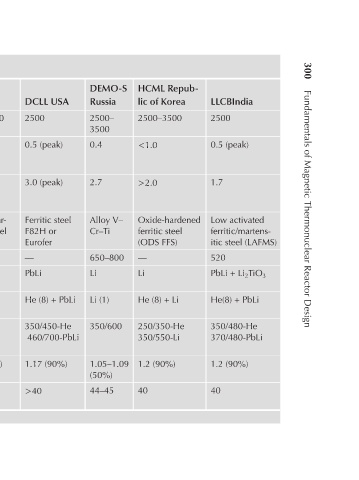
LLCBIndia 2500 0.5 (peak) 1.7 Low activated ferritic/martens- itic steel (LAFMS) 520 PbLi + Li 2 TiO 3 He(8) + PbLi 350/480-He 370/480-PbLi 1.2 (90%) 40
HCML Repub- lic of Korea 2500–3500 <1.0 >2.0 Oxide-hardened ferritic steel (ODS FFS) — Li He (8) + Li 250/350-He 350/550-Li 1.2 (90%) 40
DEMO-S Russia 2500– 3500 0.4 2.7 Alloy V– Cr–Ti 650–800 Li Li (1) 350/600 1.05–1.09 (50%) 44–45
DCLL USA 2500 0.5 (peak) 3.0 (peak) Ferritic steel F82H or Eurofer — PbLi He (8) + PbLi 350/450-He 460/700-PbLi 1.17 (90%) >40
HCLL EU 2200–3300 0.5 (peak) 2.4 (peak) Ferritic/mar- tensitic steel Eurofer 550 PbLi He (8) 300/500 1.15 (90%) 40
HCSB Japan — 0.5 3.5 Ferritic steel F82H — Li 2 TiO 3 He (10) 220/500 >1.05 (90%) 22.1–35.3
TABLE 10.2 Characteristics of the Gen-1 Blankets
DEMO-S Russia 2500–3500 0.4 2.7 Ferritic/mar- tensitic steel 9CrMoVNb — Li 4 SiO 4 He (10) 300/500 1.06 (40%) 40
HCPB EU 2200–3300 0.5 (peak) 2.4 (peak) Ferritic/mar- tensitic steel Eurofer 550 Li 4 SiO 4 He (8) 300/500 1.14 (40%) 36
Parameters Fusion power (MW) Max. surf. heat flux (MW/m 2 ) Max. neutron FW load (MW/m 2 ) Structural material FW T max (°С) Tritium breeder Coolant, P (MPa) Coolant inlet/ outlet tem- perature (°C) TBR ( 6 Li enrichment) Conversion efficiency (%)