Page 325 - Fundamentals of Magnetic Thermonuclear Reactor Design
P. 325
304 Fundamentals of Magnetic Thermonuclear Reactor Design
The plates incorporate cooling channels. The Pb–Li alloy flows radially be-
tween the plates at a rate of ∼1 mm/s (∼10 replacements of the blanket contents
a day). To reduce tritium diffusion loss through lines delivering the alloy to the
tritium processing system, diffusion barriers, reducing hydrogen permeability
4
2
10 –10 times, are foreseen.
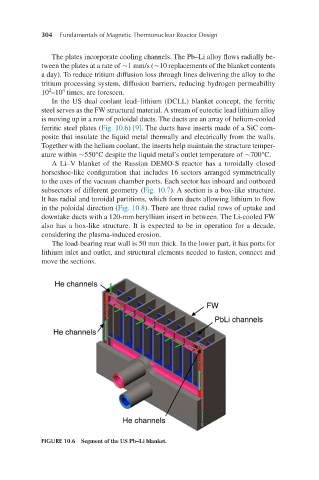
In the US dual coolant lead–lithium (DCLL) blanket concept, the ferritic
steel serves as the FW structural material. A stream of eutectic lead lithium alloy
is moving up in a row of poloidal ducts. The ducts are an array of helium-cooled
ferritic steel plates (Fig. 10.6) [9]. The ducts have inserts made of a SiC com-
posite that insulate the liquid metal thermally and electrically from the walls.
Together with the helium coolant, the inserts help maintain the structure temper-
ature within ∼550°С despite the liquid metal’s outlet temperature of ∼700°C.
A Li–V blanket of the Russian DEMO-S reactor has a toroidally closed
horseshoe-like configuration that includes 16 sectors arranged symmetrically
to the axes of the vacuum chamber ports. Each sector has inboard and outboard
subsectors of different geometry (Fig. 10.7). A section is a box-like structure.
It has radial and toroidal partitions, which form ducts allowing lithium to flow
in the poloidal direction (Fig. 10.8). There are three radial rows of uptake and
downtake ducts with a 120-mm beryllium insert in between. The Li-cooled FW
also has a box-like structure. It is expected to be in operation for a decade,
considering the plasma-induced erosion.
The load-bearing rear wall is 50 mm thick. In the lower part, it has ports for
lithium inlet and outlet, and structural elements needed to fasten, connect and
move the sections.
FIGURE 10.6 Segment of the US Pb–Li blanket.