Page 370 - Fundamentals of Magnetic Thermonuclear Reactor Design
P. 370
Power Supply Systems Chapter | 11 347
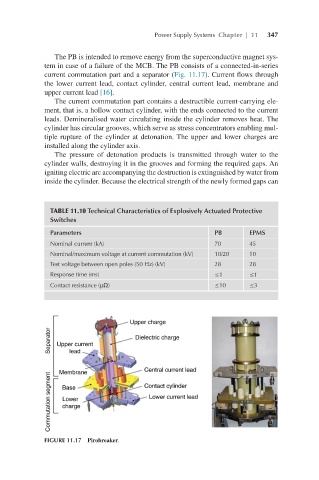
The PB is intended to remove energy from the superconductive magnet sys-
tem in case of a failure of the MCB. The PB consists of a connected-in-series
current commutation part and a separator (Fig. 11.17). Current flows through
the lower current lead, contact cylinder, central current lead, membrane and
upper current lead [16].
The current commutation part contains a destructible current-carrying ele-
ment, that is, a hollow contact cylinder, with the ends connected to the current
leads. Demineralised water circulating inside the cylinder removes heat. The
cylinder has circular grooves, which serve as stress concentrators enabling mul-
tiple rupture of the cylinder at detonation. The upper and lower charges are
installed along the cylinder axis.
The pressure of detonation products is transmitted through water to the
cylinder walls, destroying it in the grooves and forming the required gaps. An
igniting electric arc accompanying the destruction is extinguished by water from
inside the cylinder. Because the electrical strength of the newly formed gaps can
TABLE 11.10 Technical Characteristics of Explosively Actuated Protective
Switches
Parameters PB EPMS
Nominal current (kA) 70 45
Nominal/maximum voltage at current commutation (kV) 10/20 10
Test voltage between open poles (50 Hz) (kV) 28 28
Response time (ms) ≤1 ≤1
Contact resistance (µΩ) ≤10 ≤3
FIGURE 11.17 Pirobreaker.