Page 412 - Fundamentals of Magnetic Thermonuclear Reactor Design
P. 412
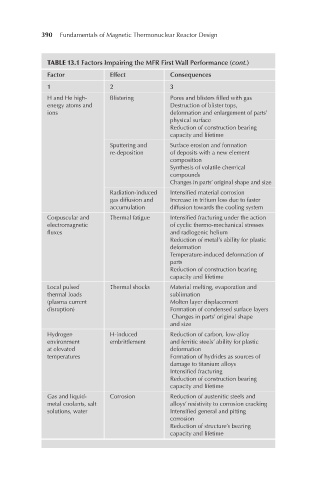
390 Fundamentals of Magnetic Thermonuclear Reactor Design
TABLE 13.1 Factors Impairing the MFR First Wall Performance (cont.)
Factor Effect Consequences
1 2 3
H and He high- Blistering Pores and blisters filled with gas
energy atoms and Destruction of blister tops,
ions deformation and enlargement of parts’
physical surface
Reduction of construction bearing
capacity and lifetime
Sputtering and Surface erosion and formation
re-deposition of deposits with a new element
composition
Synthesis of volatile chemical
compounds
Changes in parts’ original shape and size
Radiation-induced Intensified material corrosion
gas diffusion and Increase in tritium loss due to faster
accumulation diffusion towards the cooling system
Corpuscular and Thermal fatigue Intensified fracturing under the action
electromagnetic of cyclic thermo-mechanical stresses
fluxes and radiogenic helium
Reduction of metal’s ability for plastic
deformation
Temperature-induced deformation of
parts
Reduction of construction bearing
capacity and lifetime
Local pulsed Thermal shocks Material melting, evaporation and
thermal loads sublimation
(plasma current Molten layer displacement
disruption) Formation of condensed surface layers
Changes in parts’ original shape
and size
Hydrogen H-induced Reduction of carbon, low-alloy
environment embrittlement and ferritic steels’ ability for plastic
at elevated deformation
temperatures Formation of hydrides as sources of
damage to titanium alloys
Intensified fracturing
Reduction of construction bearing
capacity and lifetime
Gas and liquid- Corrosion Reduction of austenitic steels and
metal coolants, salt alloys’ resistivity to corrosion cracking
solutions, water Intensified general and pitting
corrosion
Reduction of structure’s bearing
capacity and lifetime