Page 279 - Fundamentals of Ocean Renewable Energy Generating Electricity From The Sea
P. 279
266 Fundamentals of Ocean Renewable Energy
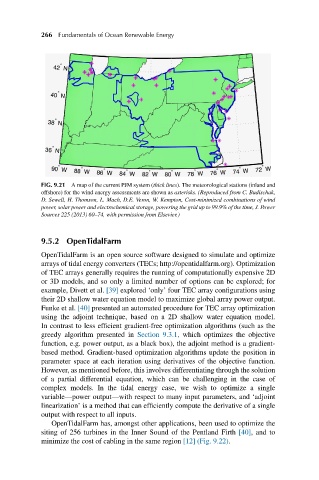
FIG. 9.21 A map of the current PJM system (thick lines). The meteorological stations (inland and
offshore) for the wind energy assessments are shown as asterisks. (Reproduced from C. Budischak,
D. Sewell, H. Thomson, L. Mach, D.E. Veron, W. Kempton, Cost-minimized combinations of wind
power, solar power and electrochemical storage, powering the grid up to 99.9% of the time, J. Power
Sources 225 (2013) 60–74, with permission from Elsevier.)
9.5.2 OpenTidalFarm
OpenTidalFarm is an open source software designed to simulate and optimize
arrays of tidal energy converters (TECs; http://opentidalfarm.org). Optimization
of TEC arrays generally requires the running of computationally expensive 2D
or 3D models, and so only a limited number of options can be explored; for
example, Divett et al. [39] explored ‘only’ four TEC array configurations using
their 2D shallow water equation model to maximize global array power output.
Funke et al. [40] presented an automated procedure for TEC array optimization
using the adjoint technique, based on a 2D shallow water equation model.
In contrast to less efficient gradient-free optimization algorithms (such as the
greedy algorithm presented in Section 9.3.1, which optimizes the objective
function, e.g. power output, as a black box), the adjoint method is a gradient-
based method. Gradient-based optimization algorithms update the position in
parameter space at each iteration using derivatives of the objective function.
However, as mentioned before, this involves differentiating through the solution
of a partial differential equation, which can be challenging in the case of
complex models. In the tidal energy case, we wish to optimize a single
variable—power output—with respect to many input parameters, and ‘adjoint
linearization’ is a method that can efficiently compute the derivative of a single
output with respect to all inputs.
OpenTidalFarm has, amongst other applications, been used to optimize the
siting of 256 turbines in the Inner Sound of the Pentland Firth [40], and to
minimize the cost of cabling in the same region [12] (Fig. 9.22).