Page 323 - Fundamentals of Ocean Renewable Energy Generating Electricity From The Sea
P. 323
Other Aspects of Ocean Renewable Energy Chapter | 10 305
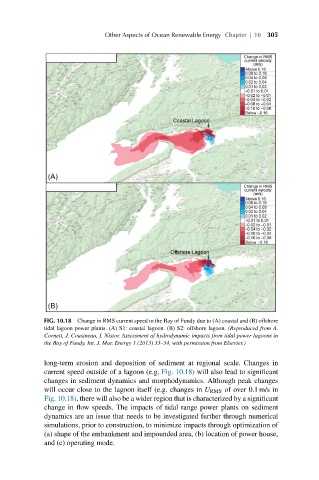
(A)
(B)
FIG. 10.18 Change in RMS current speed in the Bay of Fundy due to (A) coastal and (B) offshore
tidal lagoon power plants. (A) S1: coastal lagoon. (B) S2: offshore lagoon. (Reproduced from A.
Cornett, J. Cousineau, I. Nistor, Assessment of hydrodynamic impacts from tidal power lagoons in
the Bay of Fundy, Int. J. Mar. Energy 1 (2013) 33–54, with permission from Elsevier.)
long-term erosion and deposition of sediment at regional scale. Changes in
current speed outside of a lagoon (e.g. Fig. 10.18) will also lead to significant
changes in sediment dynamics and morphodynamics. Although peak changes
will occur close to the lagoon itself (e.g. changes in U RMS of over 0.1 m/s in
Fig. 10.18), there will also be a wider region that is characterized by a significant
change in flow speeds. The impacts of tidal range power plants on sediment
dynamics are an issue that needs to be investigated further through numerical
simulations, prior to construction, to minimize impacts through optimization of
(a) shape of the embankment and impounded area, (b) location of power house,
and (c) operating mode.