Page 139 - Fundamentals of Probability and Statistics for Engineers
P. 139
122 Fundamentals of Probability and Statistics for Engineers
5.1.1.2 Continuous Random Variables
A more frequently encountered case arises when X is continuous with known PDF,
F X (x), or pdf, f (x). To carry out the mapping steps as outlined at the beginning
X
of this section, care must be exercised in choosing appropriate corresponding
regions in range spaces R X and R Y , this mapping being governed by the transform-
ation Y g(X ). Thus, the degree of complexity in determining the probability
distribution of Y is a function of complexity in the transformation g(X ).
Let us start by considering a simple relationship
Y g
X 2X 1:
5:5
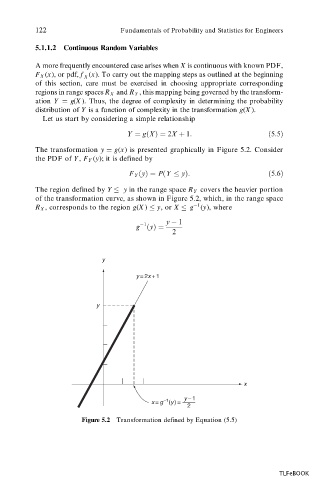
The transformation y g(x) is presented graphically in Figure 5.2. Consider
the PDF of Y , F Y (y); it is defined by
F Y
y P
Y y:
5:6
The region defined by Y y in the range space R Y covers the heavier portion
of the transformation curve, as shown in Figure 5.2, which, in the range space
1
R X , corresponds to the region g(X ) y, or X g (y), where
y
1
1
g
y
2
y
y =2x +1
y
x
y –1
–1
x = g (y)=
2
Figure 5.2 Transformation defined by Equation (5.5)
TLFeBOOK