Page 222 - Fundamentals of Probability and Statistics for Engineers
P. 222
Some Important Continuous Distributions 205
7.2.3 MULTIVARIATE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
Consider two random variables X and Y . They are said to be jointly normal if
their joint density function takes the form
" 2
1 1 x m X
f XY
x; y exp 2
2 1=2
2 X Y
1 2
1 X
x m X
y m Y y m Y 2 #)
7:27
2 ;
X Y Y
1; 1 <
x; y <
1; 1:
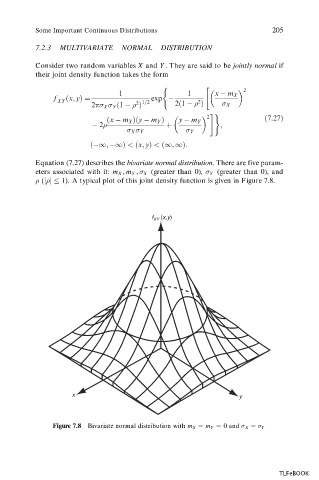
Equation (7.27) describes the bivariate normal distribution. There are five param-
eters associated with it: m X , m Y , X (greater than 0), Y (greater than 0), and
"j j 1). A typical plot of this joint density function is given in Figure 7.8.
f XY (x,y)
x y
Figure 7.8 Bivariate normal distribution with m X m Y 0 and X Y
TLFeBOOK