Page 482 - Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing
P. 482
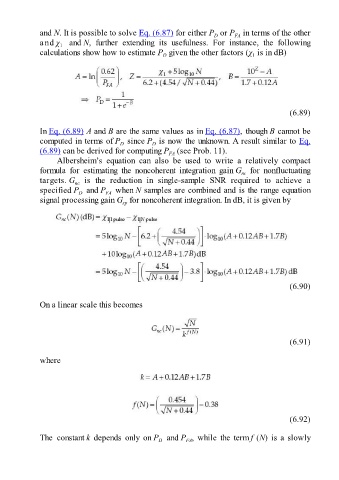
and N. It is possible to solve Eq. (6.87) for either P or P in terms of the other
D
FA
and χ and N, further extending its usefulness. For instance, the following
1
calculations show how to estimate P given the other factors (χ is in dB)
D
1
(6.89)
In Eq. (6.89) A and B are the same values as in Eq. (6.87), though B cannot be
computed in terms of P since P is now the unknown. A result similar to Eq.
D
D
(6.89) can be derived for computing P (see Prob. 11).
FA
Albersheim’s equation can also be used to write a relatively compact
formula for estimating the noncoherent integration gain G for nonfluctuating
nc
targets. G is the reduction in single-sample SNR required to achieve a
nc
specified P and P when N samples are combined and is the range equation
D
FA
signal processing gain G for noncoherent integration. In dB, it is given by
sp
(6.90)
On a linear scale this becomes
(6.91)
where
(6.92)
The constant k depends only on P and P , while the term f (N) is a slowly
FA
D