Page 108 - Fundamentals of Reservoir Engineering
P. 108
PVT ANALYSIS FOR OIL 47
R = R + (R - R ) scf / stb
s
s
p i
p
p
1 stb oil
T
rb ( oil + dissolved gas) / stb
B o
rb (free gas) / stb
s
(R - R ) B g
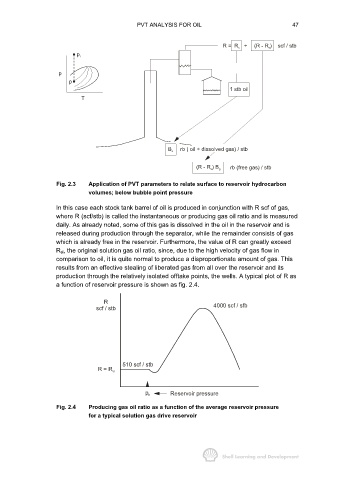
Fig. 2.3 Application of PVT parameters to relate surface to reservoir hydrocarbon
volumes; below bubble point pressure
In this case each stock tank barrel of oil is produced in conjunction with R scf of gas,
where R (scf/stb) is called the instantaneous or producing gas oil ratio and is measured
daily. As already noted, some of this gas is dissolved in the oil in the reservoir and is
released during production through the separator, while the remainder consists of gas
which is already free in the reservoir. Furthermore, the value of R can greatly exceed
R si, the original solution gas oil ratio, since, due to the high velocity of gas flow in
comparison to oil, it is quite normal to produce a disproportionate amount of gas. This
results from an effective stealing of liberated gas from all over the reservoir and its
production through the relatively isolated offtake points, the wells. A typical plot of R as
a function of reservoir pressure is shown as fig. 2.4.
R
scf / stb 4000 scf / sfb
510 scf / stb
R = R si
p b Reservoir pressure
Fig. 2.4 Producing gas oil ratio as a function of the average reservoir pressure
for a typical solution gas drive reservoir