Page 308 - Fundamentals of Reservoir Engineering
P. 308
REAL GAS FLOW: GAS WELL TESTING 244
p - from material balance
Z
p
k = 1
1
p
µ = ( )
µ
1
Z = Z( )p
1/ 2
2 1422 Qµ k Z T r 3
k
p k wf = p − ln e − + S
kh
r w 4
p k -1
k p + wf
µ = µ 2
k = 1
k k = k + 1
p + p k -1
Z k = Z wf
k > 1 2
- +
p k wf − p k wf -1 − TOL k = k + 1
accept p wf
2
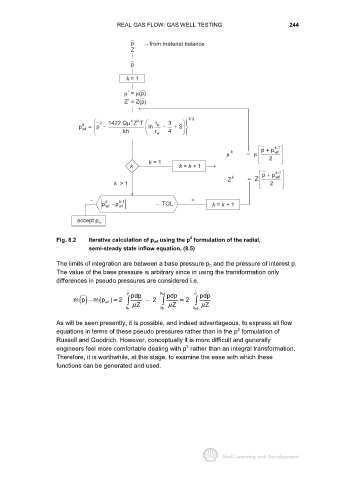
Fig. 8.2 Iterative calculation of p wf using the p formulation of the radial,
semi-steady state inflow equation, (8.5)
The limits of integration are between a base pressure p b and the pressure of interest p.
The value of the base pressure is arbitrary since in using the transformation only
differences in pseudo pressures are considered i.e.
p pdp p wf pdp p pdp
() mp
mp − ( wf ) = 2 − 2 = 2
p b µ Z p b µ Z p wf µ Z
As will be seen presently, it is possible, and indeed advantageous, to express all flow
2
equations in terms of these pseudo pressures rather than in the p formulation of
Russell and Goodrich. However, conceptually it is more difficult and generally
2
engineers feel more comfortable dealing with p rather than an integral transformation.
Therefore, it is worthwhile, at this stage, to examine the ease with which these
functions can be generated and used.