Page 99 - Fundamentals of Reservoir Engineering
P. 99
SOME BASIC CONCEPTS IN RESERVOIR ENGINEERING 38
Naturally occurring hydrocarbons are more complex than the system shown in fig. 1.14
in that they contain a great many members of the paraffin series and usually some non-
hydrocarbon impurities. Nevertheless, a phase diagram can similarly be defined for
complex mixtures and such a diagram for a typical natural gas is shown in fig. 1.15(a).
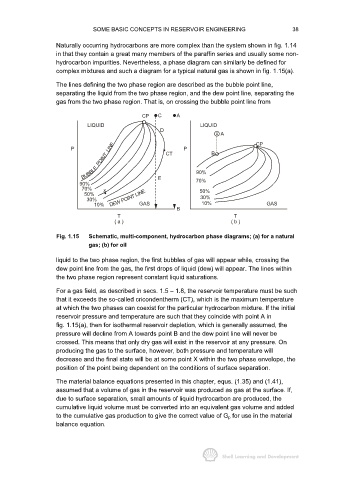
The lines defining the two phase region are described as the bubble point line,
separating the liquid from the two phase region, and the dew point line, separating the
gas from the two phase region. That is, on crossing the bubble point line from
CP C A
LIQUID LIQUID
D
A
P LINE CT P B CP
POINT
BUBBLE 90%
90% E 70%
70% x 50%
50%
30% DEW POINT LINE 30%
10% GAS 10% GAS
B
T T
( a ) ( b )
Fig. 1.15 Schematic, multi-component, hydrocarbon phase diagrams; (a) for a natural
gas; (b) for oil
liquid to the two phase region, the first bubbles of gas will appear while, crossing the
dew point line from the gas, the first drops of liquid (dew) will appear. The lines within
the two phase region represent constant liquid saturations.
For a gas field, as described in secs. 1.5 − 1.8, the reservoir temperature must be such
that it exceeds the so-called cricondentherm (CT), which is the maximum temperature
at which the two phases can coexist for the particular hydrocarbon mixture. If the initial
reservoir pressure and temperature are such that they coincide with point A in
fig. 1.15(a), then for isothermal reservoir depletion, which is generally assumed, the
pressure will decline from A towards point B and the dew point line will never be
crossed. This means that only dry gas will exist in the reservoir at any pressure. On
producing the gas to the surface, however, both pressure and temperature will
decrease and the final state will be at some point X within the two phase envelope, the
position of the point being dependent on the conditions of surface separation.
The material balance equations presented in this chapter, equs. (1.35) and (1.41),
assumed that a volume of gas in the reservoir was produced as gas at the surface. If,
due to surface separation, small amounts of liquid hydrocarbon are produced, the
cumulative liquid volume must be converted into an equivalent gas volume and added
to the cumulative gas production to give the correct value of G p for use in the material
balance equation.