Page 57 - Fundamentals of The Finite Element Method for Heat and Fluid Flow
P. 57
THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
k
k
y
k
T i T k (x , y ) 49
i
(x , y ) i T
i
j j
(x , y )
j
j
x
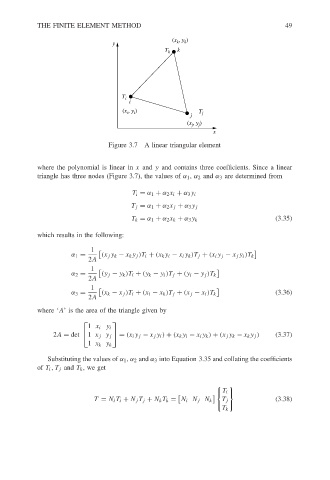
Figure 3.7 A linear triangular element
where the polynomial is linear in x and y and contains three coefficients. Since a linear
triangle has three nodes (Figure 3.7), the values of α 1 , α 2 and α 3 are determined from
T i = α 1 + α 2 x i + α 3 y i
T j = α 1 + α 2 x j + α 3 y j
T k = α 1 + α 2 x k + α 3 y k (3.35)
which results in the following:
1
α 1 = (x j y k − x k y j )T i + (x k y i − x i y k )T j + (x i y j − x j y i )T k
2A
1
α 2 = (y j − y k )T i + (y k − y i )T j + (y i − y j )T k
2A
1
α 3 = (x k − x j )T i + (x i − x k )T j + (x j − x i )T k (3.36)
2A
where ‘A’ is the area of the triangle given by
1 x i y i
= (x i y j − x j y i ) + (x k y i − x i y k ) + (x j y k − x k y j )
2A = det 1 x j y j (3.37)
1 x k y k
Substituting the values of α 1 , α 2 and α 3 into Equation 3.35 and collating the coefficients
of T i ,T j and T k ,weget
T i
T = N i T i + N j T j + N k T k = N i N j N k T j (3.38)
T k