Page 77 - Fundamentals of The Finite Element Method for Heat and Fluid Flow
P. 77
THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
y
5 y (1,6) 69
4
3
L 2
6 (3,2)
L 3
L 1
2
x x
1 (0,0)
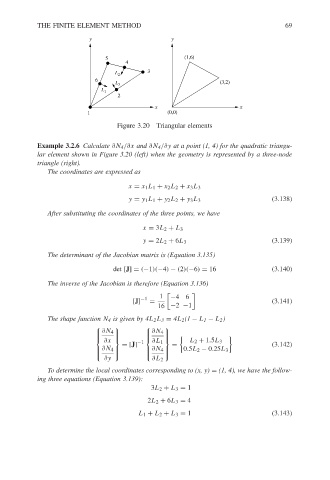
Figure 3.20 Triangular elements
Example 3.2.6 Calculate ∂N 4 /∂x and ∂N 4 /∂y at a point (1, 4) for the quadratic triangu-
lar element shown in Figure 3.20 (left) when the geometry is represented by a three-node
triangle (right).
The coordinates are expressed as
x = x 1 L 1 + x 2 L 2 + x 3 L 3
y = y 1 L 1 + y 2 L 2 + y 3 L 3 (3.138)
After substituting the coordinates of the three points, we have
x = 3L 2 + L 3
y = 2L 2 + 6L 3 (3.139)
The determinant of the Jacobian matrix is (Equation 3.135)
det [J] = (−1)(−4) − (2)(−6) = 16 (3.140)
The inverse of the Jacobian is therefore (Equation 3.136)
1 −46
−1
[J] = (3.141)
16 −2 −1
The shape function N 4 is given by 4L 2 L 3 = 4L 2 (1 − L 1 − L 2 )
∂N 4 ∂N 4
∂x −1 ∂L 1 L 2 + 1.5L 3
= [J] = (3.142)
0.5L 2 − 0.25L 3
∂N 4 ∂N 4
∂y ∂L 2
To determine the local coordinates corresponding to (x, y) = (1, 4), we have the follow-
ing three equations (Equation 3.139):
3L 2 + L 3 = 1
2L 2 + 6L 3 = 4
L 1 + L 2 + L 3 = 1 (3.143)