Page 471 - Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes : Physical, Chemical, and Biological
P. 471
426 Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes: Physical, Chemical, and Biological
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
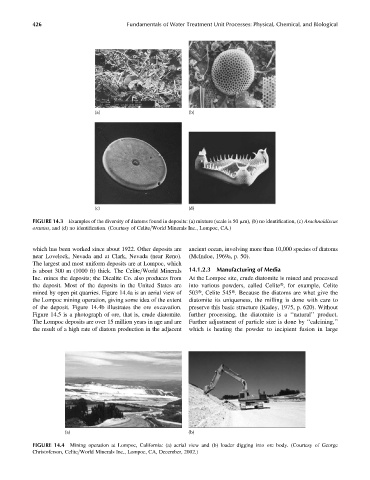
FIGURE 14.3 Examples of the diversity of diatoms found in deposits: (a) mixture (scale is 50 mm), (b) no identification, (c) Arachnoidiscus
orantus, and (d) no identification. (Courtesy of Celite=World Minerals Inc., Lompoc, CA.)
which has been worked since about 1922. Other deposits are ancient ocean, involving more than 10,000 species of diatoms
near Lovelock, Nevada and at Clark, Nevada (near Reno). (McIndoe, 1969a, p. 50).
The largest and most uniform deposits are at Lompoc, which
is about 300 m (1000 ft) thick. The Celite=World Minerals 14.1.2.3 Manufacturing of Media
Inc. mines the deposits; the Dicalite Co. also produces from At the Lompoc site, crude diatomite is mined and processed
the deposit. Most of the deposits in the United States are into various powders, called Celitet, for example, Celite
mined by open pit quarries. Figure 14.4a is an aerial view of 503t,Celite545t. Because the diatoms are what give the
the Lompoc mining operation, giving some idea of the extent diatomite its uniqueness, the milling is done with care to
of the deposit. Figure 14.4b illustrates the ore excavation. preserve this basic structure (Kadey, 1975, p. 620). Without
Figure 14.5 is a photograph of ore, that is, crude diatomite. further processing, the diatomite is a ‘‘natural’’ product.
The Lompoc deposits are over 15 million years in age and are Further adjustment of particle size is done by ‘‘calcining,’’
the result of a high rate of diatom production in the adjacent which is heating the powder to incipient fusion in large
(a) (b)
FIGURE 14.4 Mining operation at Lompoc, California: (a) aerial view and (b) loader digging into ore body. (Courtesy of George
Christoferson, Celite=World Minerals Inc., Lompoc, CA, December, 2002.)