Page 505 - Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes : Physical, Chemical, and Biological
P. 505
460 Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes: Physical, Chemical, and Biological
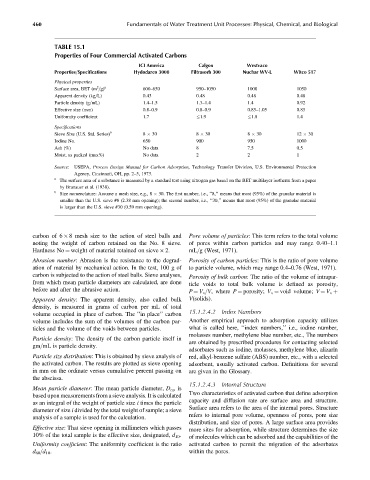
TABLE 15.1
Properties of Four Commercial Activated Carbons
ICI America Calgon Westvaco
Properties=Specifications Hydodarco 3000 Filtrasorb 300 Nuchar WV-L Witco 517
Physical properties
2
Surface area, BET (m =g) a 600–650 950–1050 1000 1050
Apparent density (kg=L) 0.43 0.48 0.48 0.48
Particle density (g=mL) 1.4–1.5 1.3–1.4 1.4 0.92
Effective size (mm) 0.8–0.9 0.8–0.9 0.85–1.05 0.85
Uniformity coefficient 1.7 1.9 1.8 1.4
Specifications
Sieve Size (U.S. Std. Series) b 8 30 8 30 8 30 12 30
Iodine No. 650 900 950 1000
Ash (%) No data 8 7.5 0.5
Moist. as packed (max%) No data 2 2 1
Source: USEPA, Process Design Manual for Carbon Adsorption, Technology Transfer Division, U.S. Environmental Protection
Agency, Cincinnati, OH, pp. 2–5, 1973.
a
The surface area of a substance is measured by a standard test using nitrogen gas based on the BET multilayer isotherm from a paper
by Branauer et al. (1938).
b
Size nomenclature: Assume a mesh size, e.g., 8 30. The first number, i.e., ‘‘8,’’ means that most (95%) of the granular material is
smaller than the U.S. sieve #8 (2.38 mm opening); the second number, i.e., ‘‘30,’’ means that most (95%) of the granular material
is larger than the U.S. sieve #30 (0.59 mm opening).
carbon of 6 8 mesh size to the action of steel balls and Pore volume of particles: This term refers to the total volume
noting the weight of carbon retained on the No. 8 sieve. of pores within carbon particles and may range 0.40–1.1
Hardness No ¼ weight of material retained on sieve 2. mL=g (West, 1971).
Abrasion number: Abrasion is the resistance to the degrad- Porosity of carbon particles: This is the ratio of pore volume
ation of material by mechanical action. In the test, 100 g of to particle volume, which may range 0.4–0.76 (West, 1971).
carbon is subjected to the action of steel balls. Sieve analyses, Porosity of bulk carbon: The ratio of the volume of intrapar-
from which mean particle diameters are calculated, are done ticle voids to total bulk volume is defined as porosity,
before and after the abrasive action.
P ¼ V v =V, where P ¼ porosity; V v ¼ void volume; V ¼ V v þ
Apparent density: The apparent density, also called bulk V(solids).
density, is measured in grams of carbon per mL of total
volume occupied in place of carbon. The ‘‘in place’’ carbon 15.1.2.4.2 Index Numbers
volume includes the sum of the volumes of the carbon par- Another empirical approach to adsorption capacity utilizes
ticles and the volume of the voids between particles. what is called here, ‘‘index numbers,’’ i.e., iodine number,
molasses number, methylene blue number, etc., The numbers
Particle density: The density of the carbon particle itself in
are obtained by prescribed procedures for contacting selected
gm=mL is particle density.
adsorbates such as iodine, molasses, methylene blue, alizarin
Particle size distribution: This is obtained by sieve analysis of red, alkyl-benzene sulfate (ABS) number, etc., with a selected
the activated carbon. The results are plotted as sieve opening adsorbent, usually activated carbon. Definitions for several
in mm on the ordinate versus cumulative percent passing on are given in the Glossary.
the abscissa.
15.1.2.4.3 Internal Structure
Mean particle diameter: The mean particle diameter, D m ,is
Two characteristics of activated carbon that define adsorption
based upon measurements from a sieve analysis. It is calculated
capacity and diffusion rate are surface area and structure.
as an integral of the weight of particle size i times the particle
Surface area refers to the area of the internal pores. Structure
diameter of size i divided by the total weight of sample; a sieve
refers to internal pore volume, openness of pores, pore size
analysis of a sample is used for the calculation.
distribution, and size of pores. A large surface area provides
Effective size: That sieve opening in millimeters which passes more sites for adsorption, while structure determines the size
10% of the total sample is the effective size, designated, d 10 . of molecules which can be adsorbed and the capabilities of the
Uniformity coefficient: The uniformity coefficient is the ratio activated carbon to permit the migration of the adsorbates
d 60 =d 10 . within the pores.