Page 51 - Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes : Physical, Chemical, and Biological
P. 51
6 Fundamentals of Water Treatment Unit Processes: Physical, Chemical, and Biological
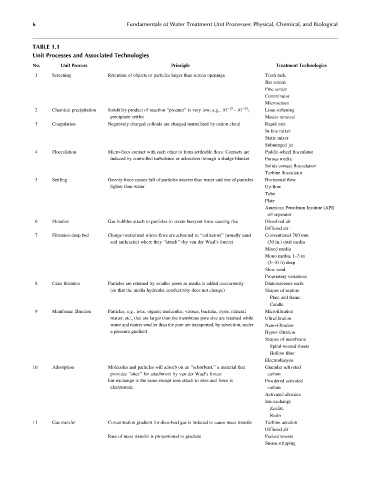
TABLE 1.1
Unit Processes and Associated Technologies
No. Unit Process Principle Treatment Technologies
1 Screening Retention of objects or particles larger than screen openings Trash rack
Bar screen
Fine screen
Comminutor
Microscreen
2 Chemical precipitation Solubility product of reaction ‘‘product’’ is very low, e.g., 10 10 10 30 ; Lime softening
precipitate settles Metals removal
3 Coagulation Negatively charged colloids are charged neutralized by cation cloud Rapid mix
In-line mixer
Static mixer
Submerged jet
4 Flocculation Micro-flocs contact with each other to form settleable flocs. Contacts are Paddle-wheel flocculator
induced by controlled turbulence or advection through a sludge blanket Porous media
Solids contact flocculation
Turbine flocculator
5 Settling Gravity force causes fall of particles heavier than water and rise of particles Horizontal flow
lighter than water Up-flow
Tube
Plate
American Petroleum Institute (API)
oil separator
6 Flotation Gas bubbles attach to particles to create buoyant force causing rise Dissolved air
Diffused air
7 Filtration-deep bed Charge neutralized micro-flocs are advected to ‘‘collectors’’ (usually sand Conventional 760 mm
and anthracite) where they ‘‘attach’’ (by van der Waal’s forces) (30 in.) dual media
Mixed media
Mono media, 1–3m
(3–10 ft) deep
Slow sand
Proprietary variations
8 Cake filtration Particles are retained by smaller pores as media is added concurrently Diatomaceous earth
(so that the media hydraulic conductivity does not change) Shapes of septum
Plate and frame
Candle
9 Membrane filtration Particles, e.g., ions, organic molecules, viruses, bacteria, cysts, mineral Microfiltration
matter, etc., that are larger than the membrane pore size are retained while Ultrafiltration
water and matter smaller than the pore are transported, by advection, under Nano-filtration
a pressure gradient Hyper-filtration
Shapes of membrane
Spiral-wound sheets
Hollow fiber
Electrodialysis
10 Adsorption Molecules and particles will adsorb on an ‘‘adsorbent,’’ a material that Granular activated
provides ‘‘sites’’ for attachment by van der Waal’s forces carbon
Ion-exchange is the same except ions attach to sites and force is Powdered activated
electrostatic carbon
Activated alumina
Ion-exchange
Zeolite
Resin
11 Gas transfer Concentration gradient for dissolved gas is induced to cause mass transfer Turbine aeration
Diffused air
Rate of mass transfer is proportional to gradient Packed towers
Steam stripping