Page 133 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 133
Gas-wetting Alteration Agent and Gas-wetting CHAPTER 3 117
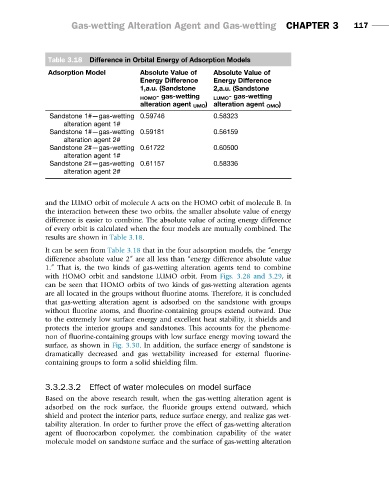
Table 3.18 Difference in Orbital Energy of Adsorption Models
Adsorption Model Absolute Value of Absolute Value of
Energy Difference Energy Difference
1,a.u. (Sandstone 2,a.u. (Sandstone
HOMO - gas-wetting LUMO - gas-wetting
alteration agent UMO ) alteration agent OMO )
Sandstone 1#—gas-wetting 0.59746 0.58323
alteration agent 1#
Sandstone 1#—gas-wetting 0.59181 0.56159
alteration agent 2#
Sandstone 2#—gas-wetting 0.61722 0.60500
alteration agent 1#
Sandstone 2#—gas-wetting 0.61157 0.58336
alteration agent 2#
and the LUMO orbit of molecule A acts on the HOMO orbit of molecule B. In
the interaction between these two orbits, the smaller absolute value of energy
difference is easier to combine. The absolute value of acting energy difference
of every orbit is calculated when the four models are mutually combined. The
results are shown in Table 3.18.
It can be seen from Table 3.18 that in the four adsorption models, the “energy
difference absolute value 2” are all less than “energy difference absolute value
1.” That is, the two kinds of gas-wetting alteration agents tend to combine
with HOMO orbit and sandstone LUMO orbit. From Figs. 3.28 and 3.29,it
can be seen that HOMO orbits of two kinds of gas-wetting alteration agents
are all located in the groups without fluorine atoms. Therefore, it is concluded
that gas-wetting alteration agent is adsorbed on the sandstone with groups
without fluorine atoms, and fluorine-containing groups extend outward. Due
to the extremely low surface energy and excellent heat stability, it shields and
protects the interior groups and sandstones. This accounts for the phenome-
non of fluorine-containing groups with low surface energy moving toward the
surface, as shown in Fig. 3.30. In addition, the surface energy of sandstone is
dramatically decreased and gas wettability increased for external fluorine-
containing groups to form a solid shielding film.
3.3.2.3.2 Effect of water molecules on model surface
Based on the above research result, when the gas-wetting alteration agent is
adsorbed on the rock surface, the fluoride groups extend outward, which
shield and protect the interior parts, reduce surface energy, and realize gas wet-
tability alteration. In order to further prove the effect of gas-wetting alteration
agent of fluorocarbon copolymer, the combination capability of the water
molecule model on sandstone surface and the surface of gas-wetting alteration