Page 129 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 129
Gas-wetting Alteration Agent and Gas-wetting CHAPTER 3 113
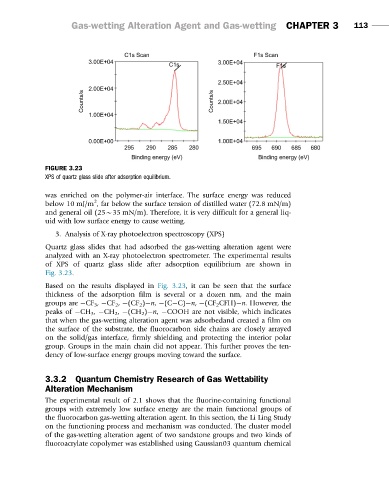
FIGURE 3.23
XPS of quartz glass slide after adsorption equilibrium.
was enriched on the polymer-air interface. The surface energy was reduced
2
below 10 mJ/m , far below the surface tension of distilled water (72.8 mN/m)
and general oil (25B35 mN/m). Therefore, it is very difficult for a general liq-
uid with low surface energy to cause wetting.
3. Analysis of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS)
Quartz glass slides that had adsorbed the gas-wetting alteration agent were
analyzed with an X-ray photoelectron spectrometer. The experimental results
of XPS of quartz glass slide after adsorption equilibrium are shown in
Fig. 3.23.
Based on the results displayed in Fig. 3.23, it can be seen that the surface
thickness of the adsorption film is several or a dozen nm, and the main
groups are CF 3 , CF 2 , (CF 2 ) n, (C C) n, (CF 2 CFH) n. However, the
peaks of CH 3 , CH 2 , (CH 2 ) n, COOH are not visible, which indicates
that when the gas-wetting alteration agent was adsorbedand created a film on
the surface of the substrate, the fluorocarbon side chains are closely arrayed
on the solid/gas interface, firmly shielding and protecting the interior polar
group. Groups in the main chain did not appear. This further proves the ten-
dency of low-surface energy groups moving toward the surface.
3.3.2 Quantum Chemistry Research of Gas Wettability
Alteration Mechanism
The experimental result of 2.1 shows that the fluorine-containing functional
groups with extremely low surface energy are the main functional groups of
the fluorocarbon gas-wetting alteration agent. In this section, the Li Ling Study
on the functioning process and mechanism was conducted. The cluster model
of the gas-wetting alteration agent of two sandstone groups and two kinds of
fluoroacrylate copolymer was established using Gaussian03 quantum chemical