Page 124 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 124
108 Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
From the contact angle test image and digital images, it can be visually seen
that there is a change in the wettability performance of the core treated with
fluoropolymer emulsion. On the untreated cores, all tested liquids spread,
except for very small contact angles for the oilfield sewage and crude oil
formed on P27. However, when the core was treated, the tested liquids don’t
entirely spread. Drops of distilled water and oilfield sewage almost present a
spherical shape on the core surface. Taking Khotan No.4, e.g., on the surface
of the core untreated by the polymer, the contact angle of water was 0.7
degrees, and on the surface of the core treated by the polymer with 35%
fluoro-mono-methacrylate (F06), the contact angle of water reaches 126.94
degrees and increases significantly. This is mainly because fluorine-containing
alkyl in the polymer bonds on the core surface and extends outside toward
the air, thereby reducing free energy on the core surface. Finally, the wettability
of core surface is transformed from strong liquid wettability to gas wettability
realizing gas-wetting alteration. However, it is worth noting that on the surface
of the core treated with polymer MPEG-b-F08 and for Khotan No.4, drops of
hexadecane were completely adsorbed, and the contact angle was 0.65 degrees.
The main reason behind this phenomenon needs to be studied further.
3.2.2.2.5 Experimental Study of Capillary Rise of Fluorine-
Containing Amphiphilic Polymer
A glass capillary was treated with fluorine-containing amphiphilic block poly-
mers, such as MPEG-b-F06, MPEG-b-F07, MPEG-b-F08, respectively. The rising
height of liquid was recorded and the contact angles were calculated, respec-
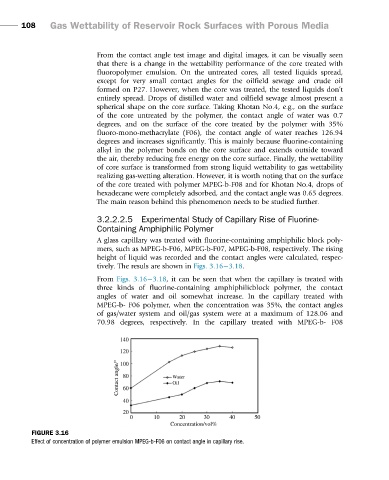
tively. The resuls are shown in Figs. 3.16 3.18.
From Figs. 3.16 3.18, it can be seen that when the capillary is treated with
three kinds of fluorine-containing amphiphilicblock polymer, the contact
angles of water and oil somewhat increase. In the capillary treated with
MPEG-b- F06 polymer, when the concentration was 35%, the contact angles
of gas/water system and oil/gas system were at a maximum of 128.06 and
70.98 degrees, respectively. In the capillary treated with MPEG-b- F08
FIGURE 3.16
Effect of concentration of polymer emulsion MPEG-b-F06 on contact angle in capillary rise.