Page 120 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 120
104 Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
C1s
O1s
MPEG-b-G04
F1s
MPEG-b-G06B F1s
O1s C1s
MPEG-b-G06C F1s
O1s C1s
1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0
Binding energy/eV
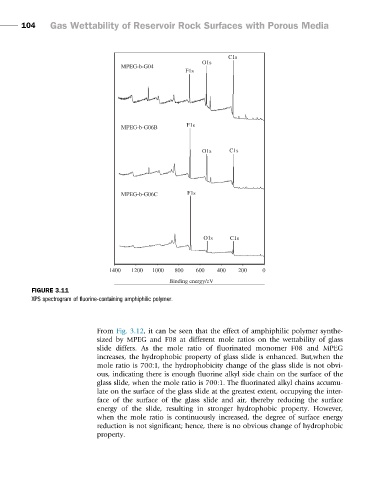
FIGURE 3.11
XPS spectrogram of fluorine-containing amphiphilic polymer.
From Fig. 3.12, it can be seen that the effect of amphiphilic polymer synthe-
sized by MPEG and F08 at different mole ratios on the wettability of glass
slide differs. As the mole ratio of fluorinated monomer F08 and MPEG
increases, the hydrophobic property of glass slide is enhanced. But,when the
mole ratio is 700:1, the hydrophobicity change of the glass slide is not obvi-
ous, indicating there is enough fluorine alkyl side chain on the surface of the
glass slide, when the mole ratio is 700:1. The fluorinated alkyl chains accumu-
late on the surface of the glass slide at the greatest extent, occupying the inter-
face of the surface of the glass slide and air, thereby reducing the surface
energy of the slide, resulting in stronger hydrophobic property. However,
when the mole ratio is continuously increased, the degree of surface energy
reduction is not significant; hence, there is no obvious change of hydrophobic
property.