Page 118 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 118
102 Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
disappears, and stretching vibration peak of C F bond appears at 1110 cm 21 ,
which indicates that all monomers participate in the polymerization.
3.2.2.2.2 Analysis of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
1 19
H NMR and F NMR nuclear magnetic resonance: The macromolecule initia-
tor MPEG-Br and fluorinated monomer F07 were combined to prepare afluor-
1
ine amphiphilic block polymeremulsion at mole ratio of 1:400. H NMR and
19
F NMR nuclear magnetic resonance of the polymer was then analyzed. The
result is shown in Figs. 3.9 and 3.10.
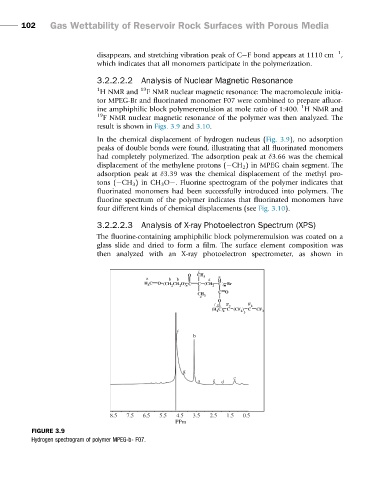
In the chemical displacement of hydrogen nucleus (Fig. 3.9), no adsorption
peaks of double bonds were found, illustrating that all fluorinated monomers
had completely polymerized. The adsorption peak at δ3.66 was the chemical
displacement of the methylene protons ( CH 2 ) in MPEG chain segment. The
adsorption peak at δ3.39 was the chemical displacement of the methyl pro-
tons ( CH 3 )inCH 3 O . Fluorine spectrogram of the polymer indicates that
fluorinated monomers had been successfully introduced into polymers. The
fluorine spectrum of the polymer indicates that fluorinated monomers have
four different kinds of chemical displacements (see Fig. 3.10).
3.2.2.2.3 Analysis of X-ray Photoelectron Spectrum (XPS)
The fluorine-containing amphiphilic block polymeremulsion was coated on a
glass slide and dried to form a film. The surface element composition was
then analyzed with an X-ray photoelectron spectrometer, as shown in
c
O CH
a b b 3 d H e
H C O (CH CH O) C C (CH C) Br
3 2 2 n 2
C O
CH
c 3
O
f,g F F 2
(H C) C 2 (CF ) C CF
2 2 2 3 3
f
b
g
c
a e d
8.5 7.5 6.5 5.5 4.5 3.5 2.5 1.5 0.5
PPm
FIGURE 3.9
Hydrogen spectrogram of polymer MPEG-b- F07.