Page 121 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 121
Gas-wetting Alteration Agent and Gas-wetting CHAPTER 3 105
FIGURE 3.12
Effect of the polymeremulsion synthesized by MPEG and F08 at different mole ratios on wettability of glass slide.
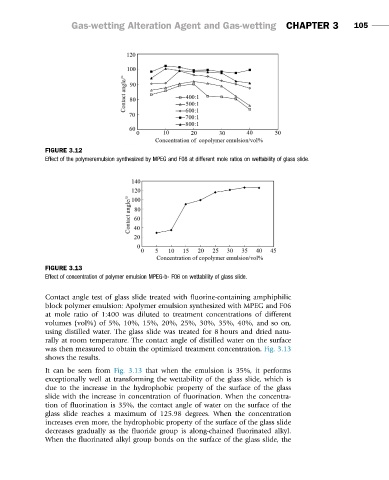
FIGURE 3.13
Effect of concentration of polymer emulsion MPEG-b- F06 on wettability of glass slide.
Contact angle test of glass slide treated with fluorine-containing amphiphilic
block polymer emulsion: Apolymer emulsion synthesized with MPEG and F06
at mole ratio of 1:400 was diluted to treatment concentrations of different
volumes (vol%) of 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25%, 30%, 35%, 40%, and so on,
using distilled water. The glass slide was treated for 8 hours and dried natu-
rally at room temperature. The contact angle of distilled water on the surface
was then measured to obtain the optimized treatment concentration. Fig. 3.13
shows the results.
It can be seen from Fig. 3.13 that when the emulsion is 35%, it performs
exceptionally well at transforming the wettability of the glass slide, which is
due to the increase in the hydrophobic property of the surface of the glass
slide with the increase in concentration of fluorination. When the concentra-
tion of fluorination is 35%, the contact angle of water on the surface of the
glass slide reaches a maximum of 125.98 degrees. When the concentration
increases even more, the hydrophobic property of the surface of the glass slide
decreases gradually as the fluoride group is along-chained fluorinated alkyl.
When the fluorinated alkyl group bonds on the surface of the glass slide, the