Page 114 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 114
98 Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
70.0
Recovery rate of imbibition/% 60.0 compare
G04-AA-DA
50.0
40.0
30.0
20.0
10.0
0.0
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
Time/min
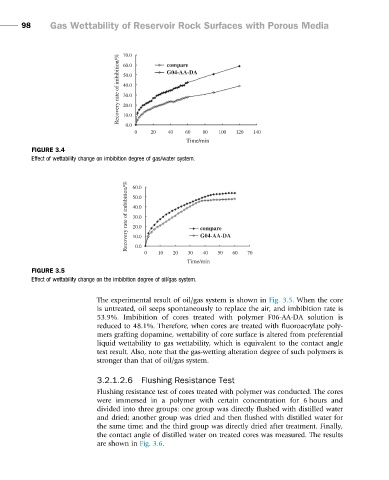
FIGURE 3.4
Effect of wettability change on imbibition degree of gas/water system.
Recovery rate of imbibition/% 50.0 compare
60.0
40.0
30.0
20.0
10.0
0.0
40
50
0 10 20 30 G04-AA-DA 60 70
Time/min
FIGURE 3.5
Effect of wettability change on the imbibition degree of oil/gas system.
The experimental result of oil/gas system is shown in Fig. 3.5. When the core
is untreated, oil seeps spontaneously to replace the air, and imbibition rate is
53.9%. Imbibition of cores treated with polymer F06-AA-DA solution is
reduced to 48.1%. Therefore, when cores are treated with fluoroacrylate poly-
mers grafting dopamine, wettability of core surface is altered from preferential
liquid wettability to gas wettability, which is equivalent to the contact angle
test result. Also, note that the gas-wetting alteration degree of such polymers is
stronger than that of oil/gas system.
3.2.1.2.6 Flushing Resistance Test
Flushing resistance test of cores treated with polymer was conducted. The cores
were immersed in a polymer with certain concentration for 6 hours and
divided into three groups: one group was directly flushed with distilled water
and dried; another group was dried and then flushed with distilled water for
the same time; and the third group was directly dried after treatment. Finally,
the contact angle of distilled water on treated cores was measured. The results
are shown in Fig. 3.6.