Page 177 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 177
Effect of Gas Wettability on the Surface Properties CHAPTER 4 161
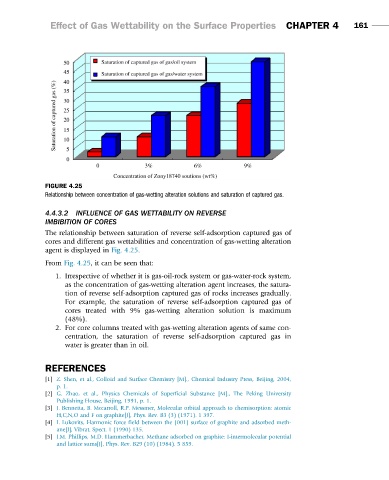
FIGURE 4.25
Relationship between concentration of gas-wetting alteration solutions and saturation of captured gas.
4.4.3.2 INFLUENCE OF GAS WETTABILITY ON REVERSE
IMBIBITION OF CORES
The relationship between saturation of reverse self-adsorption captured gas of
cores and different gas wettabilities and concentration of gas-wetting alteration
agent is displayed in Fig. 4.25.
From Fig. 4.25, it can be seen that:
1. Irrespective of whether it is gas-oil-rock system or gas-water-rock system,
as the concentration of gas-wetting alteration agent increases, the satura-
tion of reverse self-adsorption captured gas of rocks increases gradually.
For example, the saturation of reverse self-adsorption captured gas of
cores treated with 9% gas-wetting alteration solution is maximum
(48%).
2. For core columns treated with gas-wetting alteration agents of same con-
centration, the saturation of reverse self-adsorption captured gas in
water is greater than in oil.
REFERENCES
[1] Z. Shen, et al., Colloid and Surface Chemistry [M]., Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2004,
p. 1.
[2] G. Zhao, et al., Physics Chemicals of Superficial Substance [M]., The Peking University
Publishing House, Beijing, 1991, p. 1.
[3] J. Bennetta, B. Mccarroll, R.P. Messmer, Molecular orbital approach to chemisorption: atomic
H,C,N,O and F on graphite[J], Phys. Rev. B3 (3) (1971). 1 397.
[4] I. Lukovits, Harmonic force field between the (001) surface of graphite and adsorbed meth-
ane[J], Vibrat. Spect. 1 (1990) 135.
[5] J.M. Phillips, M.D. Hammerbacher, Methane adsorbed on graphite: I-intermolecular potential
and lattice sums[J], Phys. Rev. B29 (10) (1984). 5 859.