Page 243 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 243
Application of Gas Wettability CHAPTER 6 227
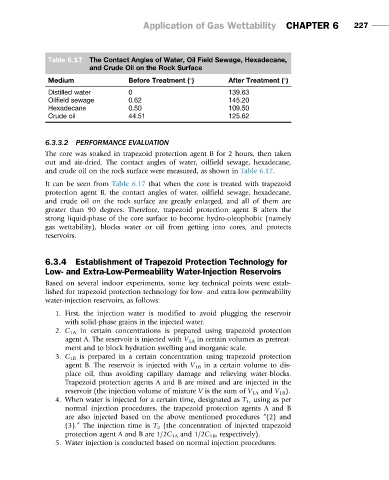
Table 6.17 The Contact Angles of Water, Oil Field Sewage, Hexadecane,
and Crude Oil on the Rock Surface
Medium Before Treatment ( ) After Treatment ( )
Distilled water 0 139.63
Oilfield sewage 0.62 145.20
Hexadecane 0.50 109.50
Crude oil 44.51 125.62
6.3.3.2 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
The core was soaked in trapezoid protection agent B for 2 hours, then taken
out and air-dried. The contact angles of water, oilfield sewage, hexadecane,
and crude oil on the rock surface were measured, as shown in Table 6.17.
It can be seen from Table 6.17 that when the core is treated with trapezoid
protection agent B, the contact angles of water, oilfield sewage, hexadecane,
and crude oil on the rock surface are greatly enlarged, and all of them are
greater than 90 degrees. Therefore, trapezoid protection agent B alters the
strong liquid-phase of the core surface to become hydro-oleophobic (namely
gas wettability), blocks water or oil from getting into cores, and protects
reservoirs.
6.3.4 Establishment of Trapezoid Protection Technology for
Low- and Extra-Low-Permeability Water-Injection Reservoirs
Based on several indoor experiments, some key technical points were estab-
lished for trapezoid protection technology for low- and extra-low-permeability
water-injection reservoirs, as follows:
1. First, the injection water is modified to avoid plugging the reservoir
with solid-phase grains in the injected water.
2. C 1A in certain concentrations is prepared using trapezoid protection
agent A. The reservoir is injected with V 1A in certain volumes as pretreat-
ment and to block hydration swelling and inorganic scale.
3. C 1B is prepared in a certain concentration using trapezoid protection
agent B. The reservoir is injected with V 1B in a certain volume to dis-
place oil, thus avoiding capillary damage and relieving water-blocks.
Trapezoid protection agents A and B are mixed and are injected in the
reservoir (the injection volume of mixture V is the sum of V 1A and V 1B ).
4. When water is injected for a certain time, designated as T 1 , using as per
normal injection procedures, the trapezoid protection agents A and B
are also injected based on the above mentioned procedures “(2) and
(3).” The injection time is T 2 (the concentration of injected trapezoid
protection agent A and B are 1/2C 1A and 1/2C 1B , respectively).
5. Water injection is conducted based on normal injection procedures.