Page 88 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 88
72 Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
ζ gas-water in air, gas wettability index of gas on the
surface of glass slide with respect to water
0.3
0.2
ζ gas-water 0.1
0.0
–25 –20 –15 –10 –5 0 5 10 15
–0.2 A Work of adhesion (mJ/m )
2
W
–0.2
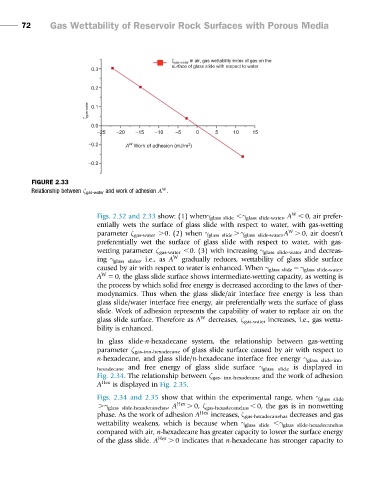
FIGURE 2.33
W
Relationship between ζ gas-water and work of adhesion A .
W
Figs. 2.32 and 2.33 show: (1) whenγ glass slide ,γ glass slide-water , A , 0, air prefer-
entially wets the surface of glass slide with respect to water, with gas-wetting
W
parameter ζ gas-water .0. (2) when γ glass slide . γ glass slide-water ,A . 0, air doesn’t
preferentially wet the surface of glass slide with respect to water, with gas-
wetting parameter ζ gas-water ,0. (3) with increasing γ glass slide-water and decreas-
ing γ glass slider ,i.e., as A W gradually reduces, wettability of glass slide surface
caused by air with respect to water is enhanced. When γ glass slide 5 γ glass slide-water ,
W
A 5 0, the glass slide surface shows intermediate-wetting capacity, as wetting is
the process by which solid free energy is decreased according to the laws of ther-
modynamics. Thus when the glass slide/air interface free energy is less than
glass slide/water interface free energy, air preferentially wets the surface of glass
slide. Work of adhesion represents the capability of water to replace air on the
glass slide surface. Therefore as A W decreases, ζ gas-water increases, i.e., gas wetta-
bility is enhanced.
In glass slide-n-hexadecane system, the relationship between gas-wetting
parameter ζ gas-inn-hexadecane of glass slide surface caused by air with respect to
n-hexadecane, and glass slide/n-hexadecane interface free energy γ glass slide-inn-
hexadecane and free energy of glass slide surface γ glass slide is displayed in
Fig. 2.34. The relationship between ζ gas- inn-hexadecane and the work of adhesion
A Hex is displayed in Fig. 2.35.
Figs. 2.34 and 2.35 show that within the experimental range, when γ glass slide
.γ glass slide-hexadecanehas , A Hex . 0, ζ gas-hexadecanehas , 0, the gas is in nonwetting
phase. As the work of adhesion A Hex increases, ζ gas-hexadecanehas decreases and gas
wettability weakens, which is because when γ glass slide ,γ glass slide-hexadecanehas
compared with air, n-hexadecane has greater capacity to lower the surface energy
of the glass slide. A Hex . 0 indicates that n-hexadecane has stronger capacity to